The Skeleton
290 likes | 447 Vues
The Skeleton. Function & Bones. Skeleton. How many bones in the body?? Does anyone know any bones in the body??. Why do we have bones??. Support – if we had no bones we would be a pile of jelly!. Why do we have bones??. Movement – Allow use to walk, run etc.

The Skeleton
E N D
Presentation Transcript
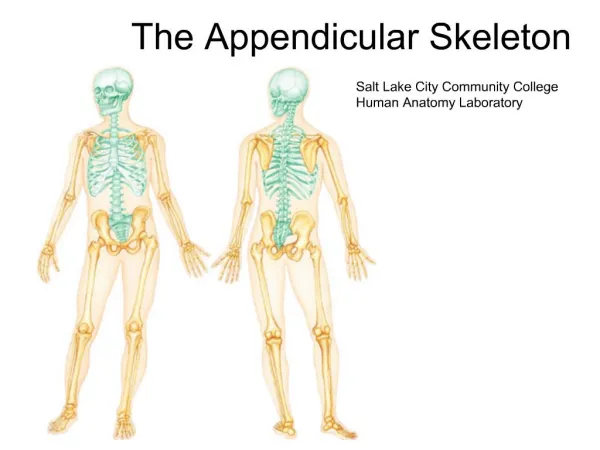
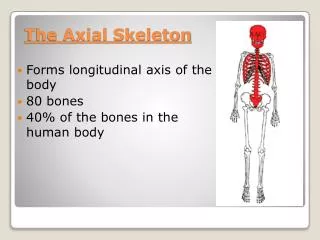
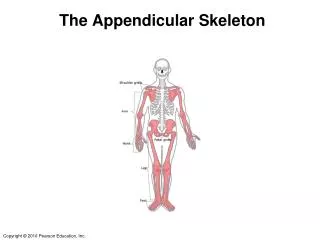
The Skeleton Function & Bones
Skeleton • How many bones in the body?? • Does anyone know any bones in the body??
Why do we have bones?? • Support – if we had no bones we would be a pile of jelly!
Why do we have bones?? • Movement – Allow use to walk, run etc. • Protection – Protects our inner organs.
The Skeleton Types of Joints
Skeletal Joints Song • https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=WHNO6D1Ee0Q
What are joints? • Joints are where bones meet & they allow for movement. • Some examples are the skull, hip, shoulder, knee, elbow.
Hinge Joints • Allows movement in one direction only. • Examples include the elbow & knee
Ball & Socket Joints • Allow movement in many directions. • Examples include the hip [between hip (socket) & top of femur (ball)] & the shoulder.
Fused Joint • No movement between the bones that meet. • An example is the skull. • The skull protects your brain
Ligaments • Join bone to bone
Questions. • Name the 3 types of joints & their function. • Give an example of each. • What does the term ligament mean?
The Skeleton Structure of Synovial Joint
Ligament! • What is a ligament from the last class?? • Ligament joins bone to bone.
Synovial Joint • A movable joint. • Examples include elbow, knee, hip.
Cartilage = A shock absorbing cushion that prevents friction between the bones. • Synovial Fluid = Lubricates the joint to allow for easy movement. • *Cartilage can be found in the spine & prevents vertebraerubbing off each other.*
The Skeleton Antagonistic Muscles
Antagonistic muscles video • https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=A4Qcjzj3Zs8
Tendon • Connects muscle to bone.
What does Antagonistic mean?? • Antagonistic = Opposing/competing. • Antagonistic muscles work opposite one another. • They work in pairs
Experiment. • Hold your arm out straight. • Which muscle contracted & which on relaxed?? • The Bicep relaxed & the tricep contracted.
Experiment. • Now hold your arm out straight & bend your elbow. • Which muscle contracted & which relaxed? • The Bicep contracted & the Tricep relaxed.
Define antagonistic muscle. • What happens when you hold your arm out straight? • What happens when you then bend your elbow? • What is a tendon?