200
510 likes | 654 Vues
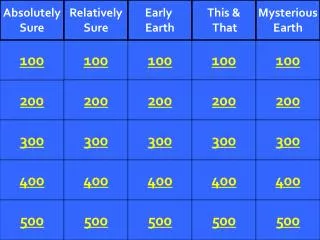
Absolutely Sure. Relatively Sure. Early Earth. This & That. Mysterious Earth. 100. 100. 100. 100. 100. 200. 200. 200. 200. 200. 300. 300. 300. 300. 300. 400. 400. 400. 400. 400. 500. 500. 500. 500. 500. Assigning a date to events or features.

200
E N D
Presentation Transcript
Absolutely Sure Relatively Sure Early Earth This & That Mysterious Earth 100 100 100 100 100 200 200 200 200 200 300 300 300 300 300 400 400 400 400 400 500 500 500 500 500
The process where unstable isotopes break down into stable isotopes of the same or other elements.
This is an atom that has the same number of protons as other atoms of the same element but that has a different number of neutrons.
I have 2,000 grams of Uranium-238. After 2 half-lives how much Uranium-238 do I have and how much Lead-206 do I have?.
What is 500 grams of Uranium-238 and 1,500 grams of Lead-206?
When talking about radioactive decay, the unstable isotopes are referred to as this.
Putting things in chronological order without actual dates and using geologic principles.
The principle that states the present is the key to the past.
An igneous intrusion is always ______ than the layers it cuts through.
A break in the geologic record created when rock layers are eroded or when sediment is not deposited for a long period of time.
The principle that states that younger rocks lie above older rocks if the layers have not been disturbed.
The force that pulled the space debris together to form Earth.
This type of energy was changed to thermal energy as material hit Earth’s surface.
When molten rock from Earth’s interior squeezes into existing rock layers and cools.
Scientists think this is created because of convection currents in the outer core.