PROTEIN SYNTHESIS
210 likes | 623 Vues
PROTEIN SYNTHESIS. PROTEIN SYNTHESIS. Protein synthesis = making protein 2 parts Transcription Translation. PROTEIN SYNTHESIS. Requires RNA RNA = Ribonucleic Acid How is this different then DNA?. PROTEIN SYNTHESIS. 3 Differences from DNA

PROTEIN SYNTHESIS
E N D
Presentation Transcript
PROTEIN SYNTHESIS • Protein synthesis = making protein • 2 parts • Transcription • Translation
PROTEIN SYNTHESIS • Requires RNA • RNA = Ribonucleic Acid How is this different then DNA?
PROTEIN SYNTHESIS • 3 Differences from DNA • Is made with ribose sugar (contains one more O2) • Single stranded • Uracil replaces thymine – therefore Adenine will bond with Uracil (A-U)
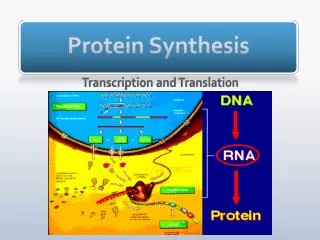
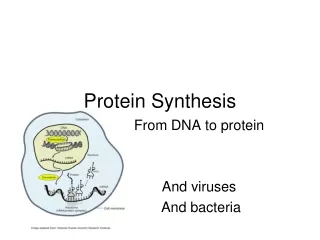
PROTEIN SYNTHESIS • 3 Types of RNA • mRNA = messenger RNA • Made from the DNA – carries the genetic info from the nucleus to the ribosomes (in cytoplasm) • Sequence of mRNA is translated into the amino acid sequence of the protein
PROTEIN SYNTHESIS • 3 Types of RNA • tRNA = transfer RNA • Carries amino acids in the cytoplasm to the ribosomes to aid in translation
PROTEIN SYNTHESIS • 3 Types of RNA • rRNA = found in ribosomes, it’s exact role is unknown but it is thought to make up the ribosomes
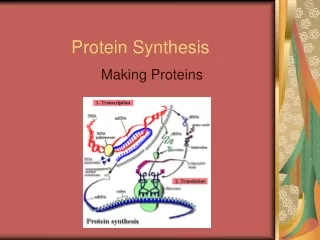
TRANSCRIPTION • Steps to creating a protein • Transcription= process of transferring genetic information from DNA to mRNA • happens in the nucleus • DNA double helix opens up (with enzymes) • a copy is made by joining complementary bases (Uracil replaces thymine)
TRANSCRIPTION • DNA = A C G T C A G T C • mRNA = U G C A G U C A G
CODONS • Determine the amino acid sequence of a protein • Every three bases = 1 amino acid = 1 codon • (ie UGC, AGU, CAG) • The order determines the protein made • There are 64 codons that direct protein synthesis
TRANSLATION • Occurs in the cytoplasm • mRNA is the template (pattern) for the order of amino acids in a protein
TRANSLATION • tRNA brings amino acids from the cytoplasm to the ribosome
TRANSLATION • tRNA has an anti-codon which corresponds with the mRNA pattern on one end and the amino acid on the other
TRANSLATION • Enzymes form a bond between the amino acids forming polypeptide chains (proteins)