Blade transmissibility by FEA
340 likes | 469 Vues
This report investigates the transmissibility of blades using Finite Element Analysis (FEA) to ensure adequate isolation in LIGO systems. It details the motivation for the study, background on previous findings, and presents the results of modal and harmonic analysis of the blades. Key factors such as eigenvalues, modal shapes, the impact of wire clamp mass, and varying damping ratios are examined. The report outlines next steps and critical discussion points to validate the methods used and assess further improvements for effective transmissibility in future designs.

Blade transmissibility by FEA
E N D
Presentation Transcript
Blade transmissibility by FEA Justin Greenhalgh, Rutherford Appleton Lab LSC, March 2004 LIGO-G040058-00-K
Contents • Report • Motivation • Background • Results • Next steps • Discussion • Is this the right way to go? • Any caveats etc?
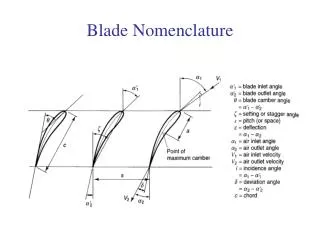
Background • Norna (ALUKGLA0010) showed that the isolation in the quads (and triples?) will be OK provided that the internal modes of the different blades are high enough and do not coincide. • Ken went on to assert (ALUKGLA0007) that high enough meant about 40 Hz. • Picture from Norna. • Will the blades give adequate isolation? • In particular, will the peaks in transmissibility caused by the internal modes overlap? • And what is the effect of the mass of the wire clamps?
So – find the actual transmissibility of the blades and multiply by the curves above (updated). (Even better, reproduce the curves above PLUS blade internal modes).
Run through T040024 • Modal analysis of reference blade • Modal analysis of blade from Conceptual design • Harmonic • No damping (cf Norna’s plot) • With damping, various damping ratios • Test effect of changing alpha on internal modes • Prestress • Add wire • Effect of wire clamp mass
T040024 • Pretty simple stuff over Christmas • Uses ANSYS macro language for ease of “what if” scenarios • Simple to write macros so that a command of the form • bf1,.48,.0045,.096,.01,20,1,1000,.050,11 • Will find the eigenvalues of a blade 0.48m long, 0.0045 thick, .096 root width, 0.01m tip width, find up to 20 eigenmodes in the range 1 to 1000 Hz, with .05kg wire clamp and 11kg mass.
T040024 • ANSYS will find • Eigenvalues and normal mode shapes • Transmissibility in a given frequency range and linear frequency step
What equations is the FE solving? • Modal analysis • Harmonic analysis • Damping
FE equations • So, use 1/(2Q) as the damping value in the ANSYS DMPRAT command.
Modal analysis of reference blade • Modal analysis of “reference” blade • Frequency has been measured at 55 Hz
Effect of adding mass at blade tip • 11 kg mass at blade tip
Harmonic • No damping • With damping, various damping ratios
Harmonic – with damping • “Zoom in” on peak by specifying restricted frequency range
Prestress Without With Little/no effect, as expected
Add wire Wire constrained laterally
Mode shapes Do any of these tie up with this peak?
Note T040025 • Revised dimensions • Easy changes allows look at a set of blades • NB resolution of peak • Results so far
Resolving the peaks… • All three blades are analysed at a background range plus an “zoom” range for each one:
Next • So far – simply testing out the methods + tools • Next – get more detailed/serious • Reference to this group – am I doing anything silly? • Check this method can reproduce Husman results • Get latest blade/wire dimensions • Check transmissibility vs measurements • Calum’s thesis? • Elsewhere? • Cross check with more detailed FE models (RAJ, MPL, others?) • Explore effect of clamp mass again • Model sloping wires • What other effects to bear in mind?
Discussion points • Reference to this group – am I doing anything silly? • Check transmissibility vs measurements • Calum’s thesis? • Elsewhere? • Cross check with more detailed FE models (RAJ, MPL, others?) • Explore effect of clamp mass again • Does this include “Norna’s curves” or do those need to be added in to the results? • What other effects to bear in mind?