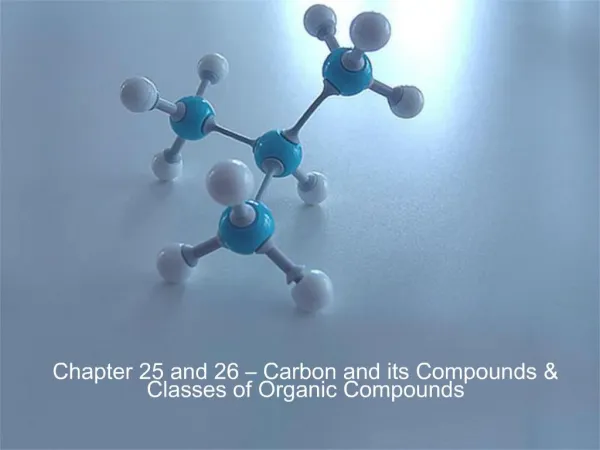
Carbon and its Compounds
E N D
Presentation Transcript
What Is Carbon ? CARBONis the chemical element with symbol C and atomic number 6. As a member of group 14 on the periodic table, it is nonmetallic and tetravalent—making four electrons available to form covalent chemical bonds. There are three naturally occurring isotopes, with 12C and 13C being stable, while 14C is radioactive
hYDROCARBONS • HYDROCARBONS are compounds of carbon and hydrogen only. • Hydrocarbons are classified based on the: • The type of bond between carbon atoms: • Single covalent bond • Double covalent bond • Tripple covalent bond
Types of hydrocarbons • SATURATED HYDROCARBON • UNSATURATED HYDROCARBON
Saturated hydrocarbons In a saturated hydrocarbon, all the bonds between carbon atoms are single bonds. Alkane is another name for a saturated hydrocarbon.
Unsaturated hydrocarbons A h y d r o c a r b o n t h a t c o n t ai n s one o r m o r e d o u b l e o r t r I p l e b o n d s I s a n u n s a tu r a t ed h y d r o c a r b o n . T h e r e a r e t h r e e t y p e s o f u n s a tu rated h y d r o c a r b o n s : a l k e n e s , a l k yn e s & a r o m a t I c h y d r o c a r b o n s .
A hydrocarbon can contain one carbon atom, as in methane or thousands of carbon atoms, as in cellulose. Straight Chains
Branched Chains Carbon has an ability to form branches with other carbon atoms. Simple branched alkanes often have a common name using a prefix to distinguish them from linear alkanes, for example n-pentane, isopentane, and neopentane. IUPAC naming conventions can be used to produce a systematic name.
Carbons can be arranged in the form of a ring or cyclic, such as CYCLOHEXANE. The Ring Or Cyclic
ALLOTROPES OF CARBON GRAPHITE DIAMOND Allotropy or allotropism is the property of some chemical elements to exist in two or more different forms, known as allotropes of these elements. Allotropes are different structural modifications of an element; the element's atoms are bonded together in a different manner. For Example -- FULLERENE
Graphite In g r a p h I t e e a c h c a r bo n a t o m Is b o n d e d t o t h r e e o t h e r Ca rbo n a t om o n t h e s a m e pl a ne I n a h e x a g o n a l A r r a y .
Fullerene This is also a form of carbon allotrope. The first one to be identified was C-60 which has carbon arranged in the shape of a football. As it resembled to the geodesic dome designed by US architect Buckminster Fuller , So the molecule was named fullerene.
Diamond In diamond, each carbon atom is tetra headedly attached to four other carbon atoms forming a rigid three dimensional structure. Thus it is the hardest substance known.
Isomers T h e o r g a n ic c o m p o u n d s w h i c h hav e s a m e m o l e c u l a r f o r m u l a b u t d i f f e r e n t s t ru c t u r a l f o r m u l a ,t h e s e a r e c a l l e d I s o m e r s a n d t h e p r o p e r t y I s c a l l e d I s o m e r I s a t i o n : EX: n –b u t a n e & I s o b u t a n e
FUNCTIONAL GROUPS In organic chemistry, functional groups are specific groups of atoms within molecules that are responsible for the characteristic chemical reactions of those molecules. The same functional group will undergo the same or similar chemical reaction(s) regardless of the size of the molecule it is a part of.
Thank You GOLCONDA GROUP T K RANDHAWA