RT-PCR lab
150 likes | 428 Vues
RT-PCR lab. You have a cell…is a certain gene on (by “on,” we mean active and producing mRNA?)? If a certain gene is on when the cell divides, the gene might produce a protein that causes cell division…. Central Dogma:. DNA has genes and is in nucleus

RT-PCR lab
E N D
Presentation Transcript
RT-PCR lab You have a cell…is a certain gene on (by “on,” we mean active and producing mRNA?)? If a certain gene is on when the cell divides, the gene might produce a protein that causes cell division….
Central Dogma: • DNA has genes and is in nucleus • TRANSCRIPTION: Double strands of DNA unwind to allow synthesis of messenger RNA (mRNA) from one strand (the coding strand) • The mRNA moves out of the nucleus to the cytoplasm • mRNA binds to Ribosomes to code for a protein- protein made (translation) • Protein carries out intent of gene (red hair protein = hair gene)
DNA is two strands of nucleotides Wrapped around each other in a double helix We sequence the DNA to find out about the genes present (later: bioinformatics lab)
Unwind, mRNA is made off DNA template- similar to this picture of DNA made off of DNA.Nucleotides pair up:G always pairs with C, T pairs with A. Except in RNA, T is replaced with U.
Transcription:RNA synthesis(note coding and template strands)(ch.21)
Transcription: Unwind 2 DNA strands and copy one making mRNA (ch.18)
So, first step of RT PCR is: • ISOLATE THE mRNA from the cell • Next, make DNA from the mRNA • This is reversing “transcription”– so use an enzyme originally obtained from viruses– ENZYME IS CALLED REVERSE TRANSCRIPTASE (THE RT OF RT PCR)
Last slide: this is the RT part of RT PCR PCR part: • After RT, you now have a tiny, trace amount of what is called complimentary DNA (cDNA). This tiny trace amount is not enough to sequence. • Next, you have to make enough copies of the tiny trace amount of cDNA to sequence
Steps in PCR (fig. 19A01): Target sequence By using Specific primers To the target Sequence
Now repeat cycle over and over Get huge number of DNA copies --enough that you can now study The gene by sequencing it (finding Order of nucleotides)
PCR: polymerase chain reaction- making many copies of cDNA • View animation of PCR: • best: • http://www.dnalc.org/ddnalc/resources/shockwave/pcranwhole.html • OK: • http://users.ugent.be/~avierstr/principles/pcrani.html • http://www.people.virginia.edu/%7erjh9u/pcranim.html • http://www.abpischools.org.uk/resources/poster-series/pcr/pcranim.asp • PCR animation links • http://www.dna.utah.edu/PCR_Animation_Links.htm
Summary of RT PCR • RT-PCR animation • http://www.bio.davidson.edu/Courses/genomics/RTPCR/RT_PCR.html
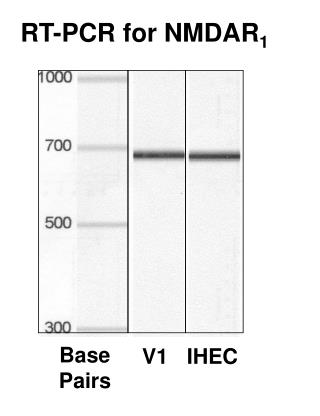
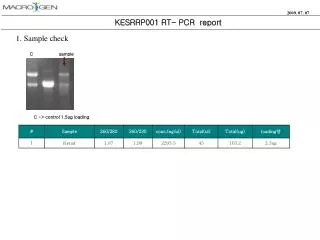
Electrophoresis to separate DNA by size (remember our prior discussion and animation): The fragment we want should be Of a known size!!