Slope Stability
960 likes | 2.18k Vues
Civil Engineering Dept. Slope Stability. Chapter (15). Dr. Jehad Hamad. 2019-2018. T ypes o f sl o pes. N a tu r al : F orm a tion du e t o g eologi c al f e a tu r es o f the e a rth M an made: Con s truct i o n activity l i k e c u t ti n g , f i l l ing e t c. I n t r od u ction.

Slope Stability
E N D
Presentation Transcript
Civil Engineering Dept. Slope Stability Chapter (15) Dr. Jehad Hamad 2019-2018
Typesof slopes • Natural : Formationduetogeologicalfeaturesof the earth • Manmade:Constructionactivitylike cutting,fillingetc
Introduction • Why do we needtounderstandthe slope failures?
Whytounderstandslopes? • Failure of naturalslopes(landslides)andman-madeslopeshave resultedinmuchdeathanddestruction • CivilEngineersareexpectedtocheck thesafetyof naturaland slopesof excavation. • Slopestabilityanalysisconsistsofdeterminingand comparing the shearstress developedalongthe potentialrupturesurfacewiththe shearstrengthof thesoil. • Attentionhas tobe paidto geology,surfacedrainage,groundwater, and theshearstrengthof soilsinassessingslopestability.
SlopeFailureTriggeringMechanisms • IntenseRain-Fall • Water-LevelChange • SeepageWaterFlow • Volcanic Eruption • EarthquakeShaking • Humanactivity
CausesofSlopefailure • Erosion:The windand flowingwatercauseserosion oftop surface of slopeandmakestheslopesteepandtherebyincreasethe tangential component ofdrivingforce. • Steady Seepage:Seepage forcesinthe slopingdirectionadd to gravityforces and make theslopesusceptibletoinstability.The pore waterpressuredecreasethe shear strength.Thisconditionis critical for thedownstreamslope. • SuddenDrawdown:in thiscase thereis reversalin thedirection flowandresultsin instabilityof sideslope.Due to sudden drawdown the shear stressesaremore due to saturatedunitweight whilethe shearingresistancedecreasesdue to porewaterpressurethatdoesnot dissipatequickly. • Rainfall:Longperiodsof rainfallsaturate,soften, anderodesoils. Waterentersintoexistingcracksand mayweakenunderlyingsoil layers,leadingtofailure,for example, mudslides.
CausesofSlopefailure…. • Earthquakes:Theyinduce dynamicshearforces. In additionthere is suddenbuildupofporewater pressurethat reducesavailableshear strength. • ExternalLoading:Additionalloadsplaced ontop of theslopeincreases thegravitationalforcesthat maycausethe slopeto fail. • Constructionactivitiesat thetoeof theslope: Excavationatthebottomof the slopingsurface willmakethe slopessteep andtherebyincreasethe gravitationalforceswhichmayresultinslope failure
Anexposedground surface that standsat anangle (b)withthehorizontal iscalled slope. • constructionofhighwayand railway • Embankments • earthdams • leveesandcanals.
TypesofSlopes FiniteSlopes • A finiteslope isone witha baseandtopsurface,theheightbeinglimited. • Theinclinedfacesofearth dams,embankmentsand excavationandthelikeareallfiniteslopes. InfiniteSlopes • Theyhave dimensionsthat extendovergreatdistances andthesoilmassisinclined tothehorizontal.
Slopestability • Types of Slopes: • Infinite slopes • Finite earth slopes • Types of Failure: • Factor of Safety: • Method of Analysis: • Swedish Arc Method • Standard Method of Slices • Bishop’s Method • Taylor’s Stability Number • Stability of Slopes of Earth Dams under Different Conditions
Factor of safety FOS = Available Shear Strength Mobilizied Shear Strength FOS can be expressed in several ways : • General. • With respect to cohesion. • With respect to friction. Slope Stability by Dr. Amizatulhani Abdullah
General factor of safety where : Fs = factor of safety with respect to strength f = average shear strength of the soil d = average shear stress developed along the potential failure surface Slope Stability by Dr. Amizatulhani Abdullah
Factor of safety with respect to cohesion Factor of safety with respect to friction Slope Stability by Dr. Amizatulhani Abdullah
Infinite slope vs finite slope Infinite slope Finite slope Slope which have great extentwith uniform soil conditions at any given depth below the surface. The soil stratum is not necessary homogenous with depth but the strata of different soils are parallel to the slope surface. Any slope with limited height. Eg: slope of embankments, cuts etc. Slope Stability by Dr. Amizatulhani Abdullah
L d a F b W
Stability of infinite slopes Stability without seepage Slope Stability by Dr. Amizatulhani Abdullah
Stability with seepage Infinite slope with steady state seepage (Das, 2002) Slope Stability by Dr. Amizatulhani Abdullah
Work example 1 An infinite slope is shown below. There is ground water seepage and the ground water table coincides with the ground surface. Determine the factor of safety, Fs. Slope Stability by Dr. Amizatulhani Abdullah
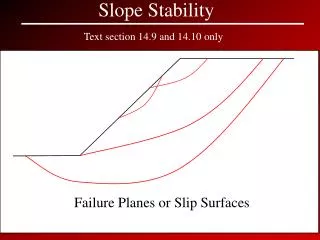
Slip orfailurezone:Itis athinzone ofsoilthat • reachesthecriticalstateor residualstateandresultsinmovementoftheupper soil mass. • Slip planeorfailureplaneorslip surfaceor • failuresurface:Itisthe surfaceofsliding. • Slidingmass:Itisthemassofsoil within the slipplane • andthe groundsurface. • Slopeangle:Itistheangle ofinclinationofa slope to thehorizontal. • The slope angleissometimesreferredtoasa ratio,for • example, 2:1 (horizontal:vertical).