Impact of Studded Tyres on Road Surface Wear and Air Quality Emissions
30 likes | 176 Vues
This study examines the direct emissions from road surface wear due to studded tyres and other vehicle-related activities, focusing on the generation of PM10 and PM2.5 particulate matter. It highlights the significance of meteorological conditions and surface retention factors in dust loading and dispersion. The role of indirect emissions, including suspended road dust and the effects of salting, sanding, and cleaning, are also analyzed. Additionally, the research discusses the influence of external airborne deposition and wind-blown dust in overall air quality impacts.

Impact of Studded Tyres on Road Surface Wear and Air Quality Emissions
E N D
Presentation Transcript
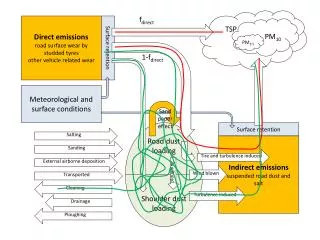
TSP fdirect Directemissions roadsurfacewear by studdedtyres othervehiclerelatedwear PM10 PM2.5 Surfaceretention 1-fdirect Meteorological and surfaceconditions Sand papereffect Road dust loading Shoulder dust loading Surfaceretention Salting Indirectemissions suspendedroad dust and salt Sanding Tire and turbulenceinduced Externalairbornedeposition Wind blown Transported ploughing Cleaning Turbulenceinduced Drainage Ploughing
TSP fdirect Directemissions roadsurfacewear by studdedtyres othervehiclerelatedwear PM10 PM2.5 Surfaceretention 1-fdirect Meteorological and surfaceconditions Sand papereffect Road dust loading Shoulder dust loading Surfaceretention Salting Indirectemissions suspendedroad dust and salt Sanding Tire and turbulenceinduced Externalairbornedeposition Wind blown Transported ploughing Cleaning Turbulenceinduced Drainage Ploughing