Beer
400 likes | 588 Vues
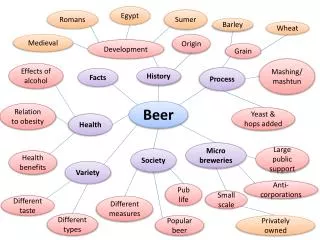
Explore the rich history of beer, tracing its origins from the Sumerians of Ancient Mesopotamia through the establishment of the first brewery in Manhattan in the 17th century to the modern beer industry. Learn about key developments such as the impact of Prohibition, the revival of brewing post-1933, and the legalization of alcohol content labeling. This overview also covers the essential ingredients for beer production—barley, hops, yeast, and water—along with the typical brewing process and the chemistry behind fermentation.

Beer
E N D
Presentation Transcript
Beer History • No True Beginning • Sumerians of Ancient Mesopotamia • First record of “Beer” • Cuneiform • Accidental discovery
U.S. Beer Timeline • 1612-1800: Beginning of Brewing in America • -The first brewery in New World established at current day Manhattan • 1800-1860: Brewing Increases in Popularity • -132 Breweries are producing 185,000 barrels of beer • 1860-1920: Brewing Becomes a Viable Industry • -IRS began taxing beer to finance the government during the Civil War • -3700 Breweries are producing 6 million barrels of beer • 1920-1933: Prohibition Days • -American Brewers Association formed • -During this time beer was outlawed
Timeline Continued • 1933-1945: Brewing is Revived -Prohibition was lifted • 1945-1980: After WWII, Prosperity Continues -Aluminum Can Introduced -Ring pull can introduced • 1980-2000: More Growth & New Aspects -Becomes legal to put the alcohol content on the bottle • 2000-Present: Still looking good -1,458 breweries product 6.2 million barrels of beer
Beer Materials • Barley • Hops • Yeast • Water
Barley • Hordeum spontaneum Wild Barley • Hordeum distichon; 2 rowed barley • Hordeum vulgaris; 6 rowed barley • Monocot; Poaceae family • One of the oldest cultivated crops in the world • Superb flavor for beer
Barley • 25% of barley produced is used for alcohol • 80% beer • 14% distilled alcohol products • 6% malted food products
Hops • Humulus lupulus • Dicot; Cannabaceae family • Minor ingredient used for adding bitterness and aroma to beer • Classified as bittering added at the beginning of brewing or as aroma hops added at the end of brewing
Yeast • Fungi • Ale yeast (top fermentation) Saccharomyces cerevisiae -Ales, Porters, Stouts, and Wheat beer • Lager yeast (bottom fermentation) S. carlsbergensis -Pilsners, Bocks, and American Malt Liquors
Water • Mineral content contributes to beer flavor • Beer is 90% water • Munich-water is high in carbonates-dark beer • Dortmund-water is high in carbonates and chloride-lagers and pale ales
Typical Beer Making Process(Bottom Fermentation) • Make Wort • Brew • Fermentation • Secondary Fermentation • Natural Carbonation
Making Wort • 2 gallons hot water 160-170 degrees F • Add 12 oz. crushed grains • Steep for 20 minutes • Add 6.6 lbs. plain light malt extract
Brewing • Add 1.5 oz. bittering hops to boiling wort • Allow to boil ~ 1hour • Add 1.5 oz. aroma hops (finishing hops) • Rapidly cool wort ~ 70 degrees • Dilute wort with water to specific volume (5 gallons)
Fermentation Process • Add 1 packet yeast to cooled wort • Let solution ferment (7-10 days) while maintaining constant temperature ~ 70 degrees • Pour (siphon) beer off of yeast
Secondary Fermentation (Optional) • Let beer sit (microscopic yeast) • Pour (siphon) beer off of yeast
Natural Carbonation • Add 5 oz. of priming sugar • Put beer in container • Let sit ~2 months for full carbonation
Chemistry • Barley has a high complement of enzymes used to convert starch into simple sugars and protein for yeast nutrition. • Hops has bacteriostatic activity that inhibits the growth of gram positive bacteria in the finished beer. • Yeast convert fermentable sugars into alcohol and carbon dioxide as a by-product.
Yeast Chemistry • yeast + sugar pyruvic acid + CO2 • pyruvic acid + 2 electrons ethanol (drinking alcohol) • Alcohol is a by-product of yeast performing glycolysis in anaerobic energy conversion
U.S. Industry Facts • 2,400 Brewers & Beer Importers • 1,908 Beer Wholesalers • 551,000 Retail Establishments • 1.78 million employees (54 billion in benefits and wages) • U.S. exports to over 100 countries
United States Beer Consumption 37% of the population are regular beer consumers 25% of adults are weekly drinkers 12% of adults are monthly drinkers 14% of adults are past year drinkers 20% of adults are less than past year drinkers 29% of adults are non drinkers Anheuser-Bush Inc.
Current United States Beer Industry 3 major leaders control 80% of the market share Anheuser-Busch Miller Brewing Adolph Coors
Arkansas Establishments • 10 Brewing • 32 Wholesaling • 2,396 Retail
Arkansas Industry • Direct Impact 5,900 Jobs $102,966,194 Wages • Supplier Impact 1,268 Jobs $41,788,442 Wages • Induced Impact 10,044 Jobs $212,870,989 Wages
Advertising • Super Bowl Ad • 1997- 1.2 million for 30 seconds • 2007- 2.6 million for 30 seconds BUD LIGHT Super Bowl Commercial
Advertising • Actually doesn’t increase total consumption • Focus is on creating brand loyalty www.postdam.edu
Most common alcohol consumption problems • Alcohol poisoning -when parts of the brain shut down because of the high amount of alcohol in the blood stream • Hangovers -Dehydration-headache -Inflammation of esophagus-heartburn -Acid accumulation in stomach-nausea -Low blood glucose levels-shakes, dizziness, blurred vision & tiredness -Intestinal inhibition- diarrhea
Problems continued • Binge Drinking • Studies suggest that binge drinking rates are declining.
Problems continued • Consuming alcohol during pregnancy can cause Fetal Alcohol Spectrum Disorder (FASD) • Fetal Alcohol Syndrome (FAS) • partial Fetal Alcohol Syndrome (pFAS) • Alcohol-Related Birth Defects (ARBD) • Alcohol-Related Neurodevelopment Disorder (ARND)
Problems Continued Drinking and Driving “In 2005, 16,885 people died in alcohol-related motor vehicle crashes, accounting for 39% of all traffic-related deaths in the United States” (NHTSA 2006). “An alcohol-related motor vehicle crash kills someone every 31 minutes and nonfatally injures someone every two minutes” (NHTSA 2006). “Each year, alcohol-related crashes in the United States cost about $51 billion” (Blincoe et al. 2002).
Organizations Resulting from Alcohol Issues • MADD- Mothers against Drunk Drivers • AA-Alcoholics Anonymous
Summary • Beer has been around for a very long time. • Alcohol is a large part of out society as a whole. • Materials • Barley, Hops, Yeast, and Water • Process • Make wort, brew, ferment, secondary ferment, natural ferment • Chemistry • Yeast forms alcohol • Benefits • Jobs (brewing, advertisement, selling, delivering etc) • People enjoy drinking beer • Drawbacks • Health related problems • Irresponsibility of drinkers
Opinion Page Did anything about the presentation surprise you? After knowing ramifications of beer, is the production and consumption good or bad for us as a society?