Perception
490 likes | 520 Vues
Perception. Perception. The organization and interpretation of our sensations. It is how we create meaning for what we see, touch, hear, feel and smell. Perception. Visual Capture: refers to the tendency for vision to dominate the other senses.

Perception
E N D
Presentation Transcript
Perception • The organization and interpretation of our sensations. It is how we create meaning for what we see, touch, hear, feel and smell.
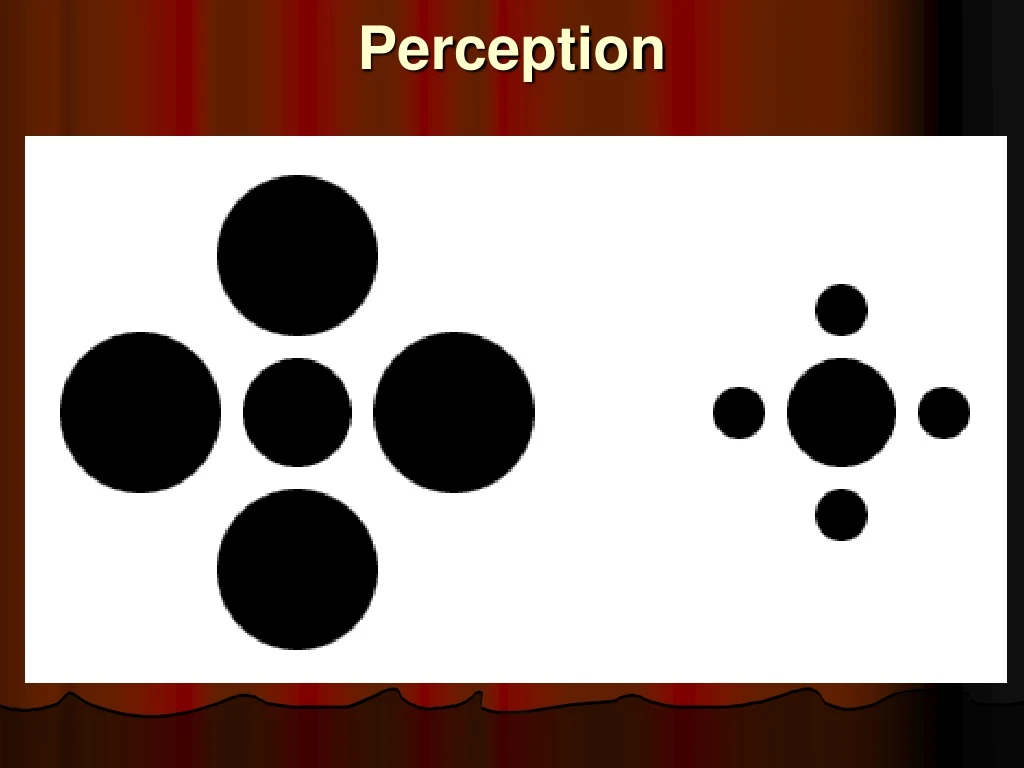
Perception • Visual Capture:refers to the tendency for vision to dominate the other senses. Does this picture help you remember the example from your book?
Perceptual Organization • Gestalt: an organized whole. • Gestalt psychologists emphasize humans’ tendencies to integrate pieces of information into meaningful wholes. • Things are not seen as sum of parts but immediately as wholes.
Gestalt Principle: Mind Always Wants to Make Stimuli Meaningful. • The fact that you can read this sentence… “it deosn't mttaer in waht oredr the ltteers in a wrod are, the olny iprometnt tihng is taht the frist and lsat ltteer be at the rghit pclae” …illustrates gestalt principles are at work to make things a meaningful whole.
Gestalt Principle: Mind Always Wants to Make Stimuli Meaningful.
Gestalt Psychology • Grouping:the perceptual tendency to organize stimuli into coherent groups • Gestault/Grouping Principles: • Proximity • Similarity • Continuity • Closure • Connectedness
Closure: tendency to fill in the gaps in visual information.
Connectedness: spots, lines and areas are seen as a unit when connected
Perceptual Organization • Figure-Ground Relationship: tendency to organize information into objects (figure) that stand out from their background(ground)
Depth Perception • Depth Perception: the ability to see objects in three dimensions. Allows us to gauge distance. • Visual Cliff: illustrated that crawling infants and newborns perceive depth.
Types of Depth Perception • Binocular Cues: depth cues that rely on the use of two eyes. • Examples of Binocular Cues: • Retinal Disparity: idea that images of an object from the two eyes differ. The closer the object, the larger the difference (disparity.) • Convergence: extent to which the eyes converge inward when looking at an object that brain keeps track of to measure distance.
Types of Depth Perception • Monocular Cues: distance cues that are available to either eye alone. Often used in art. • Examples of Monocular Cues • Relative size: smaller image is more distant • Interposition:closer object blocks distant object • Relative Clarity:hazy object seen as more distant • Texture:coarse=close; fine=distant
key name James J. GIBSON • Among the first to discover the importance of texture gradientfor perceiving depth. Most surfaces have a texture but it becomes less detailed as the surface recedes into the background.
Types of Depth Perception • Examples of Monocular Cues Continued: • Relative Height: higher objects seen as more distant • Relative Motion: closer objects seem to move faster • Linear Perspective: parallel lines converge with distance • Relative Brightness: closer objects appear brighter • Light and Shadow: nearby objects reflect more light to our eyes.
Monocular Cue? Who is closer: Snoopy or Woodstock? Woodstock How do you know? Woodstock blocks part of Snoopy. In other words, INTERPOSITION.
Monocular Cue? Less detail Further away More detail Closer
Monocular Cue? Highlights and shadows can provide information about an object's dimensions and depth. Because our visual system assumes the light comes from above, a totally different perception is obtained if the image is viewed upside down.
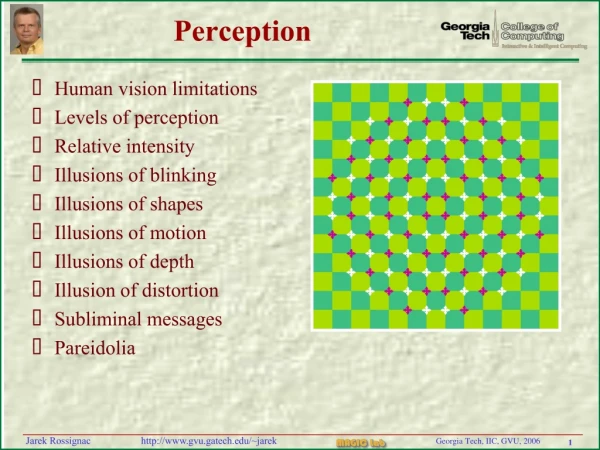
Real Quick: Phi Phenomenon • Motion Perception: Illusion of Movement with Blinking Lights
Perceptual Constancy • Perceptual Constancy: perceiving objects as unchanging despite changes in retinal image • shape • size
Interplay Between Perceived Size and Distance • Using monocular cues for distance can often cause us to perceive incorrect information.
Muller-Lyer Illusion Involves Misperception of Line Segments
Muller-Lyer Illusion is Culturally Specific to Western Architecture
Poggendorf's Optical Illusion*The single line if continued joins with the _______ line.
Poggendorf's Optical Illusion*The single line if continued joins with the red line. One explanation for this illusion is that the lower right end of the line appears nearer than the upper left; that is, the line is seen as receding in space.
Sensory Deprivation and Perception Kittens raised without exposure to horizontal lines later had difficulty perceiving horizontal bars. Remember that sensory deprivation affects infants worse than older animals and humans.
Perceptual Adaptation • Perceptual Adaptation • (vision) ability to adjust to an artificially displaced visual field • prism glasses
Perceptual Set – the power of expectancy • Perceptual Set A situation where a person is predisposed (more likely) to perceive one thing over another.
Perceptual Set* Provide punctuation that will make the words below meaningful: TIME FLIES I CANT THEYRE TOO FAST
Is there Extrasensory Perception? • Extrasensory Perception: claim that perception can occur apart from sensory input. • Telepathy • Clairvoyance • Precognition • Parapsychology: study of paranormal phenomenon, including ESP and psychokinesis.
Illusions and Phenomena The misinterpretation of the true characteristic of an object or image
Moon Illusion • The misinterpretation that the moon is larger when it is on the horizon that when it is directly overhead. • Appears to shrink as the moon rises.
Ponzo Illusion • a pair of converging lines distorts the perception of two identically sized lines. Like most visual and perceptual illusions, the Ponzo illusion helps neuroscientists study the way the brain and visual system perceive and interpret images. Artists have also utilized the illusion to great effect in their works.