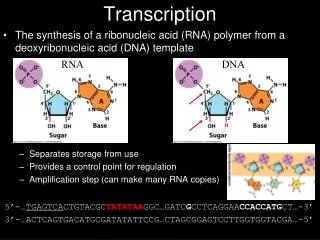
Transcription
210 likes | 328 Vues
This text explores the essential roles of messenger RNA (mRNA), ribosomal RNA (rRNA), and transfer RNA (tRNA) in protein synthesis. It details the transcription process in which an RNA copy of a DNA strand is made, explaining how enzymes unzip DNA and introduce RNA nucleotides to form mRNA. The piece also outlines the chemical differences between DNA and RNA, including their structural variations and the significance of codons in the genetic code, which determines amino acid assembly for proteins.

Transcription
E N D
Presentation Transcript
Define the following • Messenger RNA • Ribosomal RNA • Transfer RNA • Transcription • Codon
Genes and Proteins • Read on pg. 294 what role proteins play • How does DNA factor in?
RNA • 3 chemical differences between DNA and RNA • 1. Single strand • 2. Sugar in RNA is ribose • 3. Uracil (U) instead of thymine (T) • “U R single”
Three types of RNA • Messenger RNA (mRNA) • Ribosomal RNA (rRNA) • Transfer RNA (tRNA)
Messenger RNA (mRNA) • RNA that transports information from DNA in the nucleus to the cell's cytoplasm
Ribosomal RNA (rRNA) • RNA that makes up the ribosomes; • Clamps onto mRNA and • Uses it’s information to assemble amino acids in the correct order
Transfer RNA (tRNA) • RNA that transports amino acids to the ribosomes to be assembled into proteins
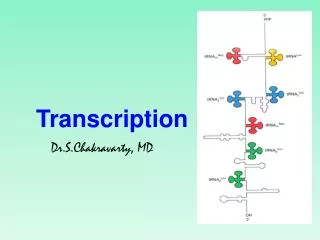
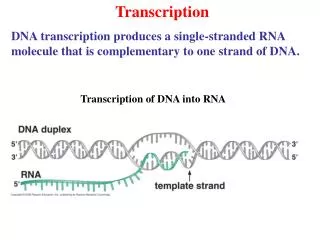
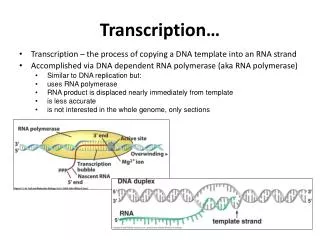
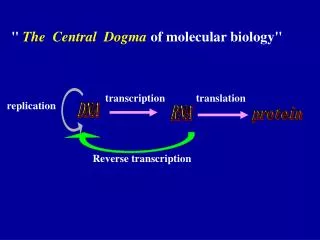
Transcription • Process in the cell nucleus where enzymes make an RNA copy of a DNA strand • 1. Enzymes unzip the molecule of DNA • 2. RNA nucleotides pair with complementary DNA nucleotides on a DNA strand
Transcription cont… • AGC TAA CCG • UCG AUU GGC • GACAAGTCCACAATC • CUGUUCAGGUGUUAG
Transcription cont… • 3. mRNA molecule breaks away as the DNA strands rejoin • mRNA leaves the nucleus and enters the cytoplasm
The Genetic Code • 4 nitrogen bases make up 20 amino acids (64 combos) • This is the genetic code • Separated into codons • Set of three nitrogen bases that codes for an amino acid