Time Series Decomposition
120 likes | 266 Vues
Explore time series decomposition, regressions, seasonal adjustment, and distinguishing deterministic and stochastic components. Learn about autocovariances, autocorrelations, dummy variables, and moving averages for forecasting.

Time Series Decomposition
E N D
Presentation Transcript
Goals • More practice working with data • Regressions and their residuals • Seasonal Adjustment
Modeling Time Series • Goal is to distinguish between the deterministic (or predictable) and stochastic (or random) parts Yt = mt + ut • mt is the deterministic component – secular trend, seasonal and cyclical movements • ut is the stochastic component Yt = Tt + Ct + St + ut
Assumptions: Random Component • Typically make three assumptions about ut • Mean zero: E(ut) = 0 • Constant variance/no covariance E(ut ut+i) = s2u if i=0 (Constant variance) E(ut ut+i) = 0 if i0 (Zero covariance) • Normally distributed ut ~ N(0, s2u)
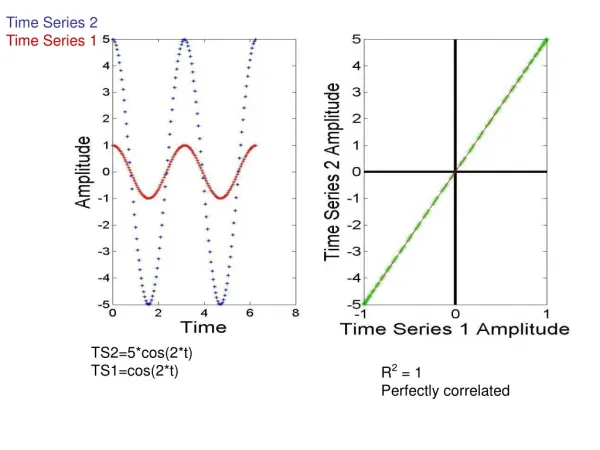
Autocovariances • Covariance between two observations • Example: kth-order autocovariance is the covariance between observations of a time series k periods apart (or lagged k periods) • Cov(Yt Yt-k) • If the autocovariances of a time series are stationary (do not change over time) then they can be used to forecast a series • Autocovariances are a measure of predictability
Autocorrelations • Closely related to autocovariances • Just the correlation between any two observations of a time series • If Cov(Yt Yt-k) is the autocovariance, then cor(Yt Yt-k) = Cov(Yt Yt-k)/var(Yt)
Dummy Variables: Trends • Uses a time variable T (=1,2,3,…) and extrapolates X along its time path Linear: Xt = a + bTt Exponential: X = ea + bTt Reciprocal: X = 1/[a + bTt] Parabolic: X = b0 + b1 Tt,+ b2T2t
Dummy Variables: Seasonal • These are “Intercept shifters” - they allow the intercept term b0 to vary systematically • Single Equation Model with Quarterly Dummies: Yt = g1Q1+g2Q2+g3Q3+g4Q4+b1X1t+…+bkX1k+ut • Can also use monthly dummies if Y is monthly • Get a different forecast for each quarter
Moving Averages • MA(q): Moving average of order q • Generally, for variable X MAqt = (Xt + Xt-1+ … +Xt-q)/q • Can also have centered moving average