Macromolecules in Biochemistry
250 likes | 298 Vues
Explore the world of macromolecules, large molecules crucial to life, made of carbon, hydrogen, and more. Learn about their origins, structure, and importance in organisms. Discover the functions and examples of carbohydrates, lipids, proteins, and nucleic acids.

Macromolecules in Biochemistry
E N D
Presentation Transcript
MACROMOLECULES • “large molecules” • Made mostly of carbon, hydrogen, and some other molecules • biochemistry is the study of these molecules that form life.
Carbon is a Versatile Atom • Carbon has four electronsin its outer shell, so it can bond to 4 other molecules.
Shape of Organic Molecules • Each type of organic molecule has a unique three-dimensional structure Thestructureof a molecule determines its functionin an organism
Macromolecules are made of many small subunits bonded together • Monomers are the individual subunits. • Polymersare made of many monomers
Where did they come from? • The primordial Earth (over 3 billion years ago) was a very different place than today • greater amounts of energy • stronger storms • many active volcanoes
There was an abundance of inorganic gases but no oxygen, and… • THERE WAS NO LIFE
Stanley Miller wanted to show that organic compounds came from inorganic chemicals present in the atmosphere at that time.
amino acids formed. • Subsequent modifications of the experiment produced all four organic macromolecule classes.
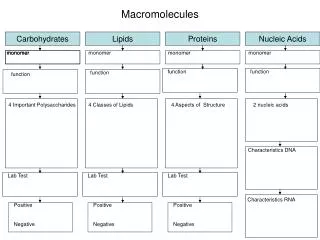
There are 4 types of macromolecules that make up all living things. • Carbohydrates • Lipids • Proteins • Nucleic acids
Carbohydrates • Function • main source of energy for cells • part of cell structure • Cellulose in cell walls of plants • Chitin in cell walls of Fungi and exoskeleton of insects • Monomer – simple sugar or glucose
Part of cell • Chloroplast • Mitochondria • Examples – • Sugar • Starch • Food sources of carbohydrates include sugar, breads, rice, pasta, etc.
Lipids • Function - • Store energy • Make up cell membranes • Makeshormones • waterproofing and insulation.
Monomer • fatty acids. • Part of cell • Cell membranes • Examples • fats, oils, waxes and steroids.
Proteins • Functions • enzymes that regulate cell processes • transport molecules across cell membranes. • Build tissues like muscle and bone • Fight infection and disease
Monomers – amino acids • Parts of cell – almost all parts of cell • Examples – food sources • Meat • Eggs • Dried beans or peas • Milk • Cheese Amino acid
Nucleic Acids • Function • DNA stores genetic information. • RNA builds proteins. • Monomer - nucleotide
Parts of cell • Chromosomes (DNA) • Ribosomes (RNA) • Nucleus • Examples - DNA & RNA
MACROMOLECULE “CUBE” • Fold construction paper as instructed • For each macromolecule: • Function • Monomer • Part of cell • Examples • Picture
MACROMOLECULE “CUBE” • Fold construction paper as instructed • For each macromolecule: • Function • Monomer • Part of cell • Examples • Picture