Topographic Maps Vocab.
120 likes | 247 Vues
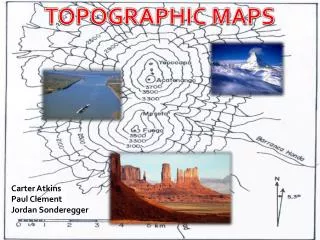
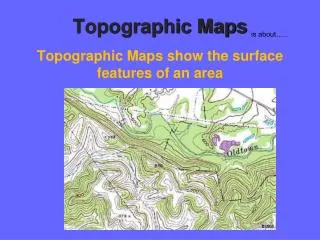
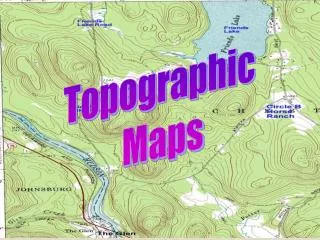
This overview of topographic maps and landforms highlights key features of Earth's surface, including lakes, streams, valleys, and mountains. It explains the concepts of wetlands—swamps, marshes, and bogs—and illustrates how contour lines represent elevation. Key terms such as contour interval, evidence, inference, and trade-offs illustrate how observations inform our understanding of natural landscapes. The information aims to enhance decision-making regarding environmental features while recognizing their importance in geography.

Topographic Maps Vocab.
E N D
Presentation Transcript
A feature of the Earth’s surface • Examples: • Lake • stream • valley • canyon • hill • ridge • mountain. Landform
General term for an area characterized by a high proportion of water and watery land. • Swamp • Marsh • Bog Wetland
Area that has a high proportion of water but dominated by trees surrounding the area. Swamp
Awetland characterized by a high proportion of water and watery land. An area that is dominated by grasses. Marsh
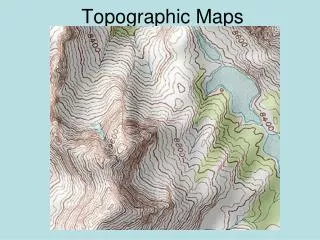
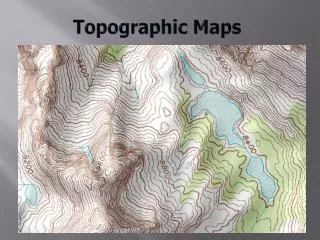
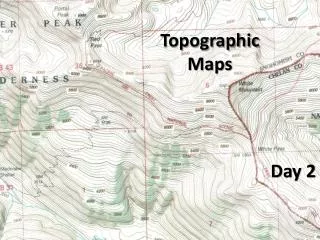
The shape of the land. Topography
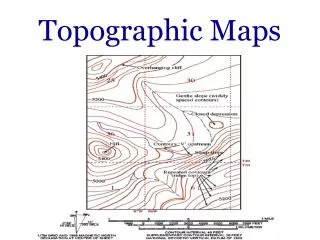
Lines that are drawn to connect all areas that are the same height relative to sea level. Contour lines
The height difference between two contour lines is the interval or change in height. Contour interval
Information gained by direct observation or from reliable sources that can be used to formulate ideas about the natural world or to inform decision-making. Evidence
To conclude by reasoning from evidence. • A lot of people have shorts on today, it must be warm out. Inference
A balancing of factors, all of which are not attainable at the same time. Getting one thing at the cost of another. The trade-off is the aspect that is given up and can only be evaluated in the context of what it was exchanged for. Trade-off
Any description or measurement gathered by the senses Observation