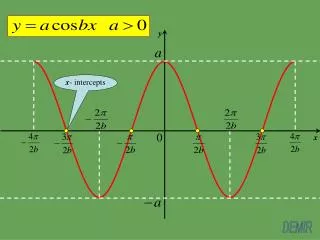
X and Y Intercepts
980 likes | 1.82k Vues
X and Y Intercepts. The y intercept is the point at which the graph of an equation crosses the y axis. y = 2x + 3. y. ( 0 , 3 ). x. The y intercept is the point at which the graph of an equation crosses the y axis. y = 2x + 3. y. Notice that the x value is zero. ( 0 , 3 ). x.

X and Y Intercepts
E N D
Presentation Transcript
The y intercept is the point at which the graph of an equation crosses the y axis. y = 2x + 3 y (0,3) x
The y intercept is the point at which the graph of an equation crosses the y axis. y = 2x + 3 y Notice that the x value is zero. (0,3) x
The x intercept is the point at which the graph of an equation crosses the x axis. y = 2x + 3 y (-3/2 ,0) x
The x intercept is the point at which the graph of an equation crosses the x axis. y = 2x + 3 y (-3/2 ,0) x Notice that the y value is zero.
Example #1 Find the y and x intercepts. Then graph the line. y = 2x + 6
Example #1 Find the y and x intercepts. Then graph the line. y = 2x + 6 y intercepty = 2(0) + 6 y = 6(0,6)
Example #1 Find the y and x intercepts. Then graph the line. y = 2x + 6 y intercepty = 2(0) + 6 y = 6(0,6) x intercept0 = 2x + 6 x = -3(-3,0)
Example #1 Find the y and x intercepts. Then graph the line. y = 2x + 6 y (0,6) (-3,0) x
Example #1 Find the y and x intercepts. Then graph the line. y = 2x + 6 y (0,6) (-3,0) x
Example #2 Find the y and x intercepts. Then graph the line. y = 3x + 12
Example #2 Find the y and x intercepts. Then graph the line. y = 3x + 12 y intercepty = 3(0) + 12 y = 12(0,12)
Example #2 Find the y and x intercepts. Then graph the line. y = 3x + 12 y intercepty = 3(0) + 12 y = 12(0,12) x intercept0 = 3x + 12 x = -4(-4,0)
Example #2 Find the y and x intercepts. Then graph the line. y = 3x + 12 y (0,12) (-4,0) x
Example #2 Find the y and x intercepts. Then graph the line. y = 3x + 12 y (0,12) (-4,0) x
For each function, find the x and y intercepts. Then graph the line.
1) y = ½ x + 4 y intercepty = ½ (0) + 4 y = 4(0,4) x intercept0 = ½ x + 4 x = -8(-8,0)
1) y = ½ x + 4 y (0,4) (-8,0) x
2) y = -2 x + 8 y intercepty = -2 (0) + 8 y = 8(0,8) x intercept0 = -2 x + 8 x = 4(4,0)
2) y = -2 x + 8 y (0,8) (4,0) x
3) y = -3x - 4 y intercepty = -3 (0) - 4 y = -4(0,-4) x intercept0 = -3 x - 4 x = -4/3(-4/3,0)
3) y = -3x - 4 y (-4/3,0) x (0,-4)
4) y = 8x - 2 y intercepty = 8 (0) - 2 y = -2(0,-2) x intercept0 = 8 x - 2 x = 1/4(1/4,0)
4) y = 8x - 2 y (1/4,0) x (0,-2)
5) 2x + 3y = 6 y intercept2(0) + 3y = 6 y = 2(0,2) x intercept2x + 3(0) = 6 x = 3(3,0)
5) 2x + 3y = 6 y (0,2) (3,0) x
6) 5x + 2y = 10 y intercept5(0) + 2y = 10 y = 5(0,5) x intercept5x + 2(0) = 10 x = 2(2,0)
6) 5x + 2y = 10 y (0,5) (2,0) x
7) -3x + 5y = 9 y intercept-3(0) + 5y = 9 y = 9/5(0,9/5) x intercept-3x + 5(0) = 9 x = -3(-3,0)
7) -3x + 5y = 9 y (0,9/5) (-3,0) x
8) -2x - 3y = 10 y intercept-2(0) - 3y = 10 y = -10/3(0,-10/3) x intercept-2x - 3(0) = 10 x = -5(-5,0)
8) -2x - 3y = 10 y (-5,0) (0,-10/3)