Evolution
210 likes | 490 Vues
Evolution. Excel Science 10 Mr. Evans. Evolution. Definition The process by which species change over time. The theory of evolution is accepted as the central theme of modern biology. Evolution.

Evolution
E N D
Presentation Transcript
Evolution Excel Science 10 Mr. Evans
Evolution • Definition • The process by which species change over time. • The theory of evolution is accepted as the central theme of modern biology.
Evolution • Evolution is a scientific theory, which is a concept that has been tested and confirmed repetitively in many ways and can be used to make predictions about the future.
Evolution • Evolution helps to explain the history of life which has been recorded in the rock layers of the Earth. • Fossils of organisms are preserved in the rocks. • The Fossil record provides clues about how organisms have existed and changed throughout Earth’s history.
The Fossil Record • The Fossil Record is a collection of fossils that record evidence of past life on the planet.
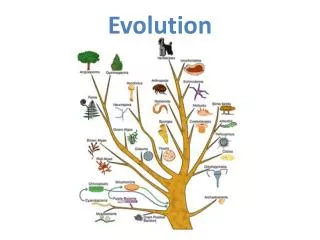
Evolutionary GrowthCladogram / Phylogenetic Tree • Evolutionary Growth is modeled as the branches of a tree. As time increases growth and change occur creating new species and extinction also occurs as some branches die.
Charles Darwin • Natural Selection • Darwin used the term natural selection to indicate that evolution occurs as a result of natural events and was not controlled by people.
Darwin’s Theory of Natural Selection • Overpopulation – more offspring produced than can survive. • Competition – limited resources – some lose competition & die. • Survival of the Fittest –“most fit” organisms survive b/c not every organism in the population was the same = • VARIATION – some have better structural or behavioral adaptations and survive! • Natural Selection – “nature”/environment determines which organisms are best adapted and will survive. • Reproduction – organisms that survive will reproduce and pass on their traits. • These traits become more common in future generations and the species will change over time. • Speciation – variations or adaptations occur in population that is geographically isolated and in diff. environments. • In time, they are too diff. to interbreed & produce fertile offspring – NOW SEPARATE SPECIES = speciation
Darwin’s Natural Selection • Individuals that survive are: • Able to reproduce • Pass their genetic information on to the next generation • Individuals that are not successful are: • Unable to reproduce • Die without leaving any offspring
Evolution • In any environment: • An individual may be born with characteristics that make it stronger, faster, or some other advantage that will help the individual survive and reproduce. • These appeared randomly • These “better” characteristics are passed on to the offspring and are likely to appear more often through oncoming generations so that eventually the species changes and all individuals possess the “better” characteristics. • The opposite occurs for less desirable characteristics
Evolution • Beneficial traits tend to become more common. • Harmful traits tend to become less common.
Evolution – Important!!!! • Populations evolve over many generations. • Result of beneficial changes occurring at random and being passed on through genetic information. • Individuals do not evolve. • An individual is born with characteristics and these do not change through one lifespan.
Sources of Variation • Mutation – change in the base sequence of a DNA molecule • Only mutations in gametes (sex cells) can become the basis for evolutionary change. • Genetic Shuffling – sexual reproduction sorts and randomly recombines genes from two different parents • Meiosis and fertilization result in new and different combinations of genes.
Results of Genetic Variation • Structural Change • The structure of any organism is the result of the entire evolutionary history of that organism. • EX: Polar Bears evolved thick fur on the soles of their feet as extra protection from the cold. • Functional Change • Molecular and biochemical changes affect how an organism works. • EX: Electric eels can produce a powerful electrical shock through their muscles to aid in the capture of food. • Behavioral Change • Certain behaviors have resulted in the benefit of the population by creating better reproductive success. • EX: Fighting among males of a walrus population allows mating to occur among the strongest and healthiest individuals.
Importance of Variation • Environmental Change • Organisms that have adapted to their environment may die if those conditions change • If all of the organisms have the same characteristics an environmental change could wipe out the entire population.
Patterns of Change • Changes in species are often related to environmental change. • Species with short reproductive cycles produce many offspring and evolve rapidly while organisms with longer reproductive cycles produce few offspring and evolve slowly. • Failure to adapt to a changing environment may result in the death of the entire species.
Rate of Evolution • Rapid environmental change results in rapid evolution. • It may take millions of years for a species to experience enough evolutionary change from its ancestors to be classified as a new species. • The number of offspring may influence the rate of evolution. • Slow – organisms that live for long periods and produce few offspring • Fast – organisms that live for short periods of time and produce many offdpring
Extinction • The disappearance of an entire species. • If the death rate exceeds the birth rate a species is susceptible to extinction. • Generally extinction is the result of environmental change. • The Fossil Record shows that throughout geologic history millions of species have come into existence, evolved, survived successfully for a time, failed to adapt to environmental change, and become extinct. • The great majority of all species that have lived on Earth have become extinct.