Smoothing Techniques in Statistical Orbit Determination: Monte Carlo Simulation Insights
270 likes | 404 Vues
This lecture explores smoothing methods used in statistical orbit determination, with a focus on the application of Monte Carlo simulations. Key concepts include the derivation of smoothed covariance equations, computational algorithms for smoothing, and the analysis of true versus filtered values. Practical examples demonstrate the calculation of root mean square (RMS) fit for smoothed data derived from a noisy sine wave. The lecture emphasizes the importance of maintaining non-negative definiteness in covariance matrices and the global consistency of filter-smoother solutions.

Smoothing Techniques in Statistical Orbit Determination: Monte Carlo Simulation Insights
E N D
Presentation Transcript
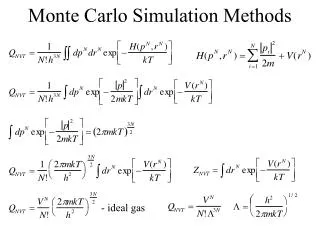
STATISTICALORBIT DETERMINATIONSmoothingMonte Carlo Simulation ASEN 5070 LECTURE 33 11/18/09
Smoothing After someafter some algebra algebra After some algebra it can be shown that
Smoothing • Finally
Smoothing The equation for the smoothed covariance is given by The equation for the smoothed covariance is given by the
Solve for the smoothed history of using the computational algorithm for smoother. Plot the true values of η, the filter values (determined by the algorithm below), and the smoothed values. Compute the RMS of the smoothed fit (data is noised single cycle of a sine wave). The sequential algorithm is given by where
The smoother covariance at stage k is given by where is the filter covariance at stage k and is the filter covariance at stage k + 1 based on k observations
Calculate the n x n difference matrix difference between the filter and smoother covariance at stage k for k {0, 1, 2, …, }. should be non negative definite, i.e. have no negative eigenvalues Denote the square root of the ith main diagonal element of as Calculate the n x 1 difference vector between the filtered and smoothed state estimate
Calculate the ratio for each i {0, 1, 2, …, n} and k {0, 1, 2, …, } If for each i and k, we have Then the filter-smoother solutions are said to be globally consistent. If for each i and k, we have The filter-smoother solutions have globally failed the consistency test.
Monte Carlo Simulation George H. Born ASEN 5070 Statistical Orbit Determination The University of Colorado, Boulder