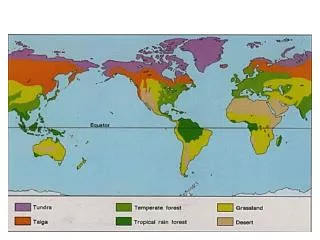
Six major land biomes
190 likes | 751 Vues
Six major land biomes . Kenzie cannon. Tundra. The tundra biome is the coldest of all eight. Key descriptions: Cold climate Poor nutrients Energy in the form of dead organic material.

Six major land biomes
E N D
Presentation Transcript
Six major land biomes Kenzie cannon
Tundra • The tundra biome is the coldest of all eight. • Key descriptions: • Cold climate • Poor nutrients • Energy in the form of dead organic material There are two types of Tundra. They are located on the north and south end of the Earth. Similar in many ways, but differ in many ways also. Arctic Tundra Northern hemisphere. Cold desert like conditions. Growing season lasts up to 60 days. The high temperature in summer is 54 degrees. The average in winter in -34 degrees. 400 different varieties of flowers. Animals are fat, with thick skin so they are able to survive through rough weather conditions. Alpine Tundra Under mountains, at high altitudes. Trees can not grow in the Alpine. Growing season is approximately 180 days. Vegetation is similar to the Arctic Biome. Every night, the temperature drops to below freezing.
Tropical Rain Forest • Located 28 degrees north or south of the equator. • A very rain nourished biome. • The rainforest is often referred to as the Earths lungs, because of the amount of oxygen that is created within the biome. • Rainforests are the home of half of the living organisms in the world. • There are 4 types of Tropical Rainforests. • Located within • Asia • Australia • Africa • South and Central America • Mexico Lowland equatorial evergreen rainforests: High rainfall (80 inches annually) Simi-evergreen seasonal forests: Receive high levels of rainfall, but include trees that lose leaves in the winter. Montane rainforests: Found in cooler-climate mountainous areas. Flooded forests: Includes freshwater swamps.
Grasslands Grasslands are a large amount of land, exploding with terrains of grass, flowers, and herbs. Precipitation levels are high enough to keep grass growing, and occasionally a few trees. The chances of a fire striking are extremely large and dangerous. Contains over 80 different types of species, 300 species of birds, and flowers. Two types of Grassland biomes: Tall grass: Extremely humid Very wet Short grass: Low precipitation Hot summers Cold winters
Taiga Animal life: The animal life within this biome, is very thin and scares because of the harsh weather conditions. Some examples of animals are listed below. Lynx, wolverines, bobcats, rabbits, and elk. Introduction: The taiga is a needle leaf forest. The climate is cold and lonely. Food shortages occur in winter, because of the increased drop of vegetation. Animals either hibernate or fly south during the freezing cold winters, with the few animals it contains that is. Taiga, got its name from the language of Russian which means forest, obviously. Weather conditions: The taiga is normally below freezing six months out of every year. During winter the range of the temperatures are anywhere from -65 degrees to 30 degrees fahrenheit. In summer the high could possibly be 70 degrees, with the chance of a low at 20 degrees fahrenheit. Tree life: Many different trees can not support themselves, with the freezing temperatures. The few trees located there are the coniferous trees.
Desert Background: Within the desert, there holds little to no water. Knowing that water is essential to life, you would assume the animal life is close to none, as with plant life. Which is true, in a sense. There are some animals that can survive, but they only come out at night, which is when the sand is cooler. There are two types of deserts, hot and dry deserts, and cold deserts. Temperature: Hot and dry desert temperatures: Anywhere from 20 to 25 degrees celsius. Cold desert temperatures: Anywhere from 21 to 26 degrees celsius. Animal life: Hot and dry desert life: Small nocturnal carnivores, insects, spiders, and birds. Cold desert life: Antelope, ground squirrels, and kangaroo rats. Precipitation: Hot and dry desert annual rainfall: 15 centimeters on average per year. Cold desert annual rainfall: 15 to 26 centimeters average per year.
Temperate forest Location: Major areas in which the temperate forest is located is within South America, Russia, Japan, and Eastern China. Levels of the forest: 1.Tree stratum level: This zone is anywhere from 60 to 100 feet tall. 2. Small, sapling tree zone: This zone holds the young and short trees. 3.The shrub zone: Holds all the shrubs within the ecosystem. 4. The herb zone: This zone houses all the herbal plants. 5. The ground zone: This zone contains all the mosses and bacteria growing. Temperature: The annual temperature is 50 degrees fahrenheit. Precipitation: The average amount of rainfall every year is anywhere from 30 to 60 inches.
Fresh water biome Information: There are many examples of fresh water biomes. They are located all over the world. They can be man made, or created by nature. There are four major examples of fresh water biomes. Streams: Lakes: Rivers: Ponds: This is a moving strip of water also. It is made up of a sides referred to as banks, and the bottom of the river which is the bed. Sometimes two small rivers will collide and create one large river. This is a moving strip of water. The streams drain the Earth of water that is unneeded. A majority of the runoff from precipitation goes into streams. This is a small hole in the ground that collects water. Plants grow along side of them, they are full of nutrients in which plants feed off of. The bottom of the pond, is usually made up of mud. This is a body of water that is much larger than any of the other examples given. Sometimes lakes are so large, they contain waves within them. In summer time the top layer of the water is always warm but, underneath is surprisingly cold.
Salt water biome About 70 percent of the Earth is covered in a salt water biome. Many organisms within this biome live. The picture shown is a representation of the Earth, containing all of its oceans. Many benefits are presented to us by the ocean. Such as entertainment, energy, food, and a source of water.
Work Cited http://www.ucmp.berkeley.edu/exhibits/biomes/tundra.php Information on the tundra location http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Tropical_rainforest Information on the Tropical Rainforest http://www.blueplanetbiomes.org/grasslands.htm Grassland information location http://www.blueplanetbiomes.org/taiga.htm Information on Taiga listed above. http://www.blueplanetbiomes.org/desert.htmInformation on the desert biome. http://www.bioexpedition.com/freshwater-biome.htmlInformation on the freshwater biomes http://www.blueplanetbiomes.org/deciduous_forest.htmInformation on the temperate forest http://www.kidcyber.com.au/topics/ocean.htm Information on the salt water biomes