General Atmospheric Circulation
320 likes | 463 Vues
This text explores the fundamental concepts of atmospheric circulation and its impact on climate. It explains how Earth, being a tilted sphere, experiences uneven heating from the sun, which leads to the formation of seasons and global wind patterns. Key topics include the balance of forces acting on atmospheric flow, such as pressure gradients and the Coriolis effect, and their role in geostrophic flow. Additionally, it highlights the significance of circulation zones like trade winds and the intertropical convergence zone, illustrating their influence on global vegetation patterns and climate zones.

General Atmospheric Circulation
E N D
Presentation Transcript
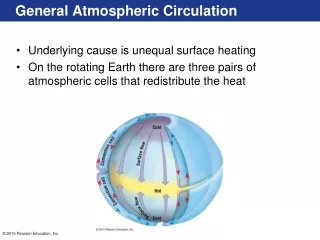
General Atmospheric Circulation V1003 - Science and Society
Take away concepts and ideas The Earth is heated unevenly. Why there are seasons. Global-scale wind patterns. Geostrophic flow: Balance of forces that act on atmospheric flow (Pressure gradients & gravity balanced by Coriolis force) Wind belts and climate zones. Monsoonal climate.
Seasonal changes in solar energy winter summer winter summer winter summer
The equation of state (air) Atmospheric Pressure is a function of temperature and density Ideal Gas Law: P = R T if pressure is constant, then what happens to as T increases?
Pressure imbalance = flow 1. Pressure imbalance is a FORCE (F = m x a) 2. Law of mass continuity (empty spaces not tolerated in fluids)
Earth’s uneven radiation • Earth is a sphere (uneven radiation) • Tilted (there are seasons) Sphere means equator gets more radiation than poles. Tilt mean the amount of radiation at one location changes with time (seasons).
Q1: Knowing uneven heating and P = R T • Poles have low pressure, equator has high pressure? b) Equator has low pressure, poles have high pressure?
BUT - The Earth rotates Apparent (inertial) forces control the flow of air in response to these pressure gradients. Centripedal force is the force acting on body by string Centrifugal force is the opposite force acted on by the ball (by its own inertia)
Imagine a satellite in orbit Centripetal force = Gravity Centrifugal force = mass and acceleration of satellite Exact balance sets the angular velocity of the satellite
The Coriolis Force Artifact of Earth’s rotation An apparent force which acts on motion on the earth’s surface Conservation of angular momentum Fcoriolis = 0 on equator, increases poleward
… the pressure gradient force (∆P) is balanced by Coriolis force. Applies to atmosphere and ocean circulation where friction can be ignored. Geostrophic Balance
Geostrophic balanceBalance between pressure and coriolis forces
Geostrophic Balance NORTHERN HEMISPHERE
Geostrophic flow in the Northern Hemisphere Counter-clockwise around low pressure cells Clockwise around high pressure cells
An example of Geostrophic flow Low High
Burlington Q2: What direction is the wind coming FROM in Burlington, VT today? • North • East • West • South
Application to Earth Geostrophic flow gives rise to banded circulation zones
Trade Winds and the Intertropical Convergence Zone (ITCZ) ITCZ
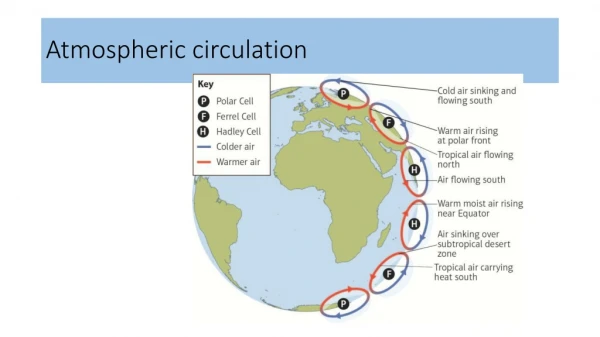
Hadley Cell Tropical convection cells westerlies Trade winds Hadley Cell Trade winds
Global vegetation patterns Rising limb of Hadley Cell (ITCZ) = Rainforest Descending limb of Hadley Cell = Deserts