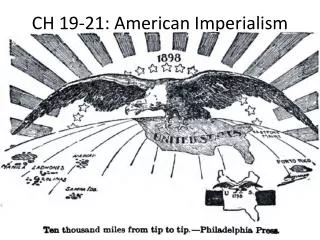
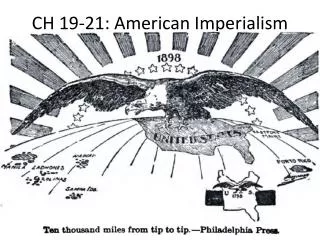
U.S. Imperialism: Spanish-American War, Philippine Insurrection, and Expansion Policies
280 likes | 418 Vues
This document explores U.S. imperialism in the late 19th and early 20th centuries, focusing on key events such as the Spanish-American War and the Philippine Insurrection. It delves into the debates over American expansionism, including the Roosevelt Corollary to the Monroe Doctrine and the establishment of the Panama Canal. The impacts on territories like Cuba and Puerto Rico are examined, alongside the motivations behind U.S. foreign policy, such as economic interests and military strategy. Essential questions prompt an analysis of these historical events' legacy.

U.S. Imperialism: Spanish-American War, Philippine Insurrection, and Expansion Policies
E N D
Presentation Transcript
AKS • 43a - describe the Spanish-American War, the Philippine insurrection, and the Constitutional debate over American expansionism • 43b - explain U.S. involvement in Latin America, as reflected by the Roosevelt Corollary to the Monroe Doctrine and the creation of the Panama Can
Essential Questions • 18.1 • How did the U.S. expand its influence around the world? Why? • What were the major events and policies that relate to this imperialism?
Activator • Get with a partner and name as many U.S. territories as possible!!!
Imperialism • Imperialism—policy of extending control over weaker nations • Thirst for new markets • Desire for military strength • Belief in cultural superiority
Alaska • 1867, arranges purchase of Alaska from Russia for $7.2 million • Alaska rich in timber, minerals, oil
Hawaii • Since 1790s, U.S. merchants stop in Hawaii on way to China, India • 1887, U.S. pressures Hawaii to allow naval base at Pearl Harbor • With help of marines, business groups overthrow Queen Liliuokalani • Set up government headed by Sanford B. Dole • President Cleveland cannot make Dole surrender power to queen • recognizes Republic of Hawaii • Under President McKinley, Congress proclaims Hawaii U.S. territory
18.2 • The Spanish American War • What was the Spanish American War? • Who were the major actors? • Why is it important?
Spanish-American War Review • What was the De Lome Letter (book)? • Where was the first battle? • What future President was par of the Rough Riders? • What happened to Cuba, Puerto Rico, the Philippines, and Guam after the war?
18.3 • Essential Questions • What were the stories behind U.S. Imperialism in the early 20th Century? • What was the Philippine Insurrection? What happened? • What do you think?
Puerto Rico • Puerto Rico under military rule after Spanish-American War • 1900, Foraker Act sets up civil government • president appoints governor • 1917, Puerto Ricans made U.S. citizens
Cuba • U.S. makes Cuba add Platt Amendment to its 1901 constitution • Platt Amendment does not allow Cuba to go into debt; also stipulates • no treaties that let foreign power control land • U.S. has right to intervene • U.S. can buy, lease land for navy • Protectorate—country whose affairs partly controlled by stronger one • What does this mean for Cuba?
Review • What did the Foraker act do? • What are three stipulations of the Platt Amendment? • What is a protectorate? • How did isolationists feel about adding new territory?
Philippine Insurrection • Filipinos outraged at Treaty of Paris call for annexation • What war did the Treaty of Paris end? • 1899, Emilio Aguinaldo leads fight for independence against U.S. • 20,000 Filipinos die in fight for independence; estimates of up to 1 million civilians • July 4, 1946, Philippines become independent
U.S. Interest in China • U.S. sees China as vast potential market, investment opportunity • Why they thought the Pacific was so important!!! • U.S. Secretary of State John Hay issues Open Door notes • Notes ask imperialist nations to share trading rights with U.S. • U.S. has right to keep markets open • U.S., Britain, France, Germany, Japan put down Boxer Rebellion
Review • Explain the Philippine Insurrection in one sentence… • 1 minute – write it down • Why was the U.S. interested in China? What did this have to do with territory in the Pacific?
What do you think? • Get with a partner and come up with 3 pros and 3 cons to U.S. expansionism/imperialism • You have 5 minutes
19.4 • What was the role of Teddy Roosevelt and Woodrow Wilson and the world (we will learn more about Wilson with WWI)? • What is their legacy today?
Teddy and the Panama Canal • U.S. wants canal to cut travel time of commercial, military ships • Construction of canal is one of world’s greatest engineering feats • Before the canal, a ship from San Francisco to NY would have to travel 18,200 miles! • http://www.5min.com/Video/Learn-about-the-Panama-Canal-38365794
Teddy and the World • Roosevelt fears European intervention if Latin America defaults • Reminds Europeans of Monroe Doctrine, demands they stay out • What was the Monroe Doctrine? • Roosevelt Corollary—U. S. to use force to protect economic interests • “Speak softly and carry a big stick” – Big Stick Diplomacy • Dollar diplomacy—U.S. guarantees foreign loans by U.S. business
What does the graph show? Were U.S. policies in Central America effective?
Review • What was the benefit of the Panama Canal? • What was the Monroe Doctrine? • Under what policy did the U.S. become the “policeman” of Latin American Nations?