Transformers
180 likes | 458 Vues
Transformers. What?. Power stations produce high voltage electricity about 25kV A transformer will ‘step up’ this voltage to about 400kV before the electricity is put through over head cables. Why?.

Transformers
E N D
Presentation Transcript
What? • Power stations produce high voltage electricity about 25kV • A transformer will ‘step up’ this voltage to about 400kV before the electricity is put through over head cables
Why? • When a current passes through a wire, friction causes the wire to get hot. The more current passing through the wire the hotter it gets. • A transformer that has ‘stepped up’ the voltage will also have ‘stepped down’ the current.
How? • Example. Drax power station produces a given amount of energy. Lets estimate that every second Drax is pumping out 4000,000,000J of energy • Energy can not be created or destroyed • All the energy that goes into a transformer should come out (less any losses)
V P = 450 000 000W V = 25 000V Using P = IV I = P/V I = 450000000 250000 I = 1800A
Transformers What is a transformer? Where are transformers used? What do we call a transformer that increases voltage? What do we call a transformer that decreases voltage? A device used to increase or decrease voltage On the National Grid, household appliances STEP-UP Transformer STEP-DOWN Transformer
How electricity gets to your home…. Power station Step-up transformer National Grid Step-down transformer Homes, businesses and factories etc
Why bother with transformers? riction When electrical current flows you get f_____ in the conductor. With friction you always get h___. This heat is wasted e____. You get more wasted energy at low v______ than high voltages. So the electricity is increased in voltage before it is transferred to the N_____ G__. In this way less energy is lost. Then, when it gets to your home, a school or a factory, the voltage is stepped d___. eat nergy oltages ationalrid own
Step-down More/less turns on the primary coil than the secondary coil. Primary Secondary
Step-up More/less turns on the primary coil than the secondary coil. Primary Secondary
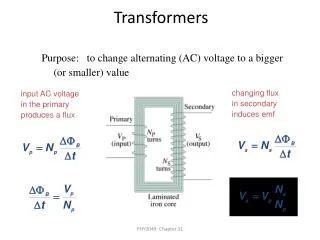
Transformer calculations The size of the output voltage depends upon the ratio of the turns on the primary and secondary coils. Guess what? There’s a formula (it is Physics after all!) - V1 = N1 V2 = N2 V – voltage N - number of turns
Transformer Question 1 • A transformer has 200 turns on its primary coil and 50 turns on its secondary coil. The input voltage is 920V. • Is is a step-up or step-down transformer? • What is the output voltage? Step-down 230V
Transformer Question 2 • A transformer has 100 turns on its primary coil. It has an input voltage of 35V and an output voltage of 175V. • Is is a step-up or step-down transformer? • How many turns are on the secondary coil? Step-up 500turns