Market Equilibrium
80 likes | 193 Vues
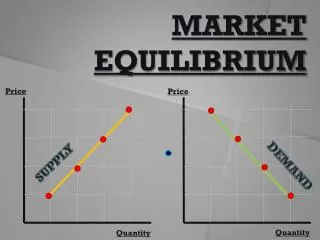
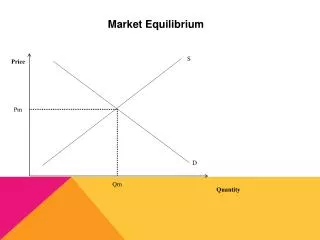
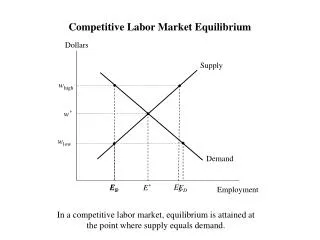
Market equilibrium occurs when the supply of a product meets its demand at a specific price. In this state, there is neither excess demand nor excess supply, indicating that producers manufacture exactly what consumers demand. This concept demonstrates how shifts in supply or demand can alter equilibrium price and quantity. Factors such as increased demand or reduced supply can raise prices, while decreased demand or increased supply can lower prices. Understanding these fluctuations is crucial for businesses and consumers in navigating market changes effectively.

Market Equilibrium
E N D
Presentation Transcript
What is it? • When the supply of a product is equal to the demand of a product at a certain price. • This means that there is no excess demand or supply. That is, producers do not make more or less product than what consumers demand, at a certain price point.
S D Excess supply Excess demand
The demand curve shifts to the right. 1)This means there is an increase or decrease in demand? 2)What is the new equilibrium price? Is it higher or lower? 3)If firm refused to increase supply from the original equilibrium price would there be excess supply or excess demand. 4) By how much? S D1 D2
S An decrease in demand Lowers/ increases Equilibrium price and Raises/ lowers Equilibrium quantity D1 D2 D2
S1 S2 An increase in supply Lowers/ increases Equilibrium price and Raises/ lowers Equilibrium quantity D
S2 An decrease in supply Lowers/ increases Equilibrium price and Raises/ lowers Equilibrium quantity S1 D