Principles of Nucleic Acid Structure
300 likes | 602 Vues
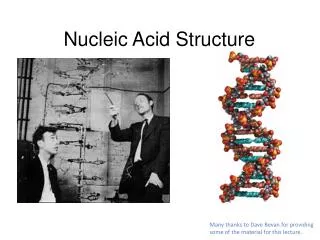
Principles of Nucleic Acid Structure. September 11, 2008. Components of Nucleic Acid Structures. Sugar Base Phosphate. Bases. Pyrimidines and purines Positions of hydrogens key to recognition. Tautomeric structures. Keto vs inol Different hydrogen bonding patterns. pK of nucleotides.

Principles of Nucleic Acid Structure
E N D
Presentation Transcript
Principles of Nucleic Acid Structure September 11, 2008
Components of Nucleic Acid Structures • Sugar • Base • Phosphate
Bases • Pyrimidines and purines • Positions of hydrogens key to recognition
Tautomeric structures • Keto vs inol • Different hydrogen bonding patterns
pK of nucleotides • Affects hydrogen bonding possibilities N1 adenine-3.5 N3 cytosine-4.2 N7 of adenine 1.0
Geometry of Watson Crick base pairsA:T and G:C are isosteric
Hydrogen bonding if WC base pair • Definition of Major and Minor groove • Mechanisms of recognition
Basepair-base • C-G-C (C must be protonated) • T-A-T normal • Found in triple helices
Conformation wheel for nucleotides • -3 values • -3 values • -3 values • -two ranges • C3’ endo • C2’ endo • -trans,g- • -3 values
Common building blocksSmall changes leading to big differences
References Saenger, Wolfram. Principles of Nucleic Acid Structure. Springer-Verlag New York Inc., 1984, pp. 109, 113. Neidle, Stephen. Nucleic Acid Structure and Recognition. Oxford University Press, 2002, pp. 18, 21-22, 34, 36, 68, 90, 165-166. Voet, Donald and Judith G. Biochemistry. John Wiley & Sons, 1990, pp. 792, 797, 807-809.