Respiratory Function Tests
130 likes | 612 Vues
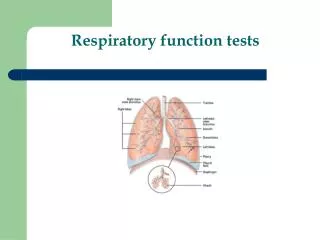
Respiratory Function Tests. Fiona Gilmour SHO 03/06/04. Respiratory Function Tests. Mechanical Function Spirometry Lung Volumes Diffusion Capacity Gas Exchange Function Arterial Blood Gases. Use?. Do not predict individual risk of pulmonary complications Smoking Exercise tolerance

Respiratory Function Tests
E N D
Presentation Transcript
Respiratory Function Tests Fiona Gilmour SHO 03/06/04
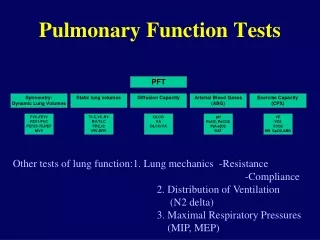
Respiratory Function Tests • Mechanical Function • Spirometry • Lung Volumes • Diffusion Capacity • Gas Exchange Function • Arterial Blood Gases
Use? • Do not predict individual risk of pulmonary complications • Smoking • Exercise tolerance • Type of surgery • Those who benefit pre-op • Equivocal clinical or CXR findings to aid Dx • Functional ability cannot be assessed eg Physically disabled • Thoracic resections - specific requirements • Most useful for monitoring response to therapy/ following progress of disease
Validity depends on • Co-operation and technique of patient • Experience of operator • Quality of equipment • Various patterns overlap so difficult to interpret
Lung Volumes • VT = volume breathed in and out in relaxed breathing • IRV = extra volume that can be inhaled with maximum effort • ERV = extra volume expired with maximum effort • IRV+VT+ERV = Vital capacity (VC) • ERV+RV = Functional residual capacity (FRC)
Spirometry 2 • FEV1 = volume exhaled in 1 second • FVC = total forced volume exhaled • FEV1/FVC% • PEF = Peak expiratory flow during forced expiration • All values compared to predicted values based on • Age • Sex • Height +/or weight • Race
Spirometry 3 • Specific disease patterns can be seen based on these values • Obstructive • Restrictive • Normal FEV1/FVC is 80% • If obstructive picture found response to bronchodilators is measured
Expiratory Flow • Measured on spirometer or peak flow meter • Compared with predicted values • Reduced values indicate airflow obstruction • If diary kept indicates current fitness • Maximum flow rates at different stages of VC can also be measured • indicates small airway function • PEF <200L/min effective cough is difficult
Diffusion Capacity • Carbon monoxide diffusing capacity (DLCO) is rate of transfer of CO from inspired gas to pulmonary capillary (transfer factor) • Indicates health of alveolar-capillary membrane • Useful for evaluation of Emphysema • Does not indicate gas exchange • Measured by single breath test • RV can be measured at the same time using Helium
Relevance to Thoracic • Need to assess cardiorespiratory reserve • Can estimate post op lung function • Needs to be considered in context of patients health and proposed resection • 3 Groups • Fit, good exercise tolerance, normal spirometry • major med probs, min ex tol, grossly abnormal spirometry • Mod coexisting disease, reduced ex tol, abnormal spirometry
Cont. • Post op estimate FEV1 <800L or FVC < 15ml/kg increases risk, difficult to cough and may need ventilation • Post op estimate = Pre op value x (5 - no.lobes resected) / 5 • Goal is post op value FEV1 > 35% predicted • Minimum pre op FEV1 • Pneumonectomy >55% • Lobectomy >40% • Wedge >35%