Evolution of Forest Modelling Paradigms: From Biology to Empiricism
120 likes | 218 Vues
Explore the classification and evolution of forest modeling rooted in the contributions of biologists, mathematicians, and foresters, shaping disciplines such as bioclimatology, fractal geometry, and forest mensuration. Uncover the chessboard of static and dynamic vegetation models, empirical and functional-structural tree models, and the significance of forest ecosystems in contemporary modeling practices. Engage in a journey through the intricate tapestry of forest modeling paradigms and their interdisciplinary applications within ecological sciences.

Evolution of Forest Modelling Paradigms: From Biology to Empiricism
E N D
Presentation Transcript
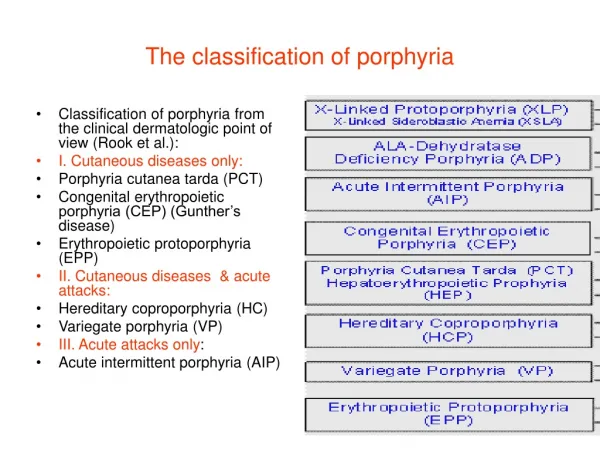
At genesis of forest modelling the three Wisemenhave operated : The first has been called BIOLOGIST and searched for answer to: „Why tree organs growth?“ He gave to world: algorithm of photosynthesis Gift has been accepted in disciplines: bioclimatology, ecopedology, plant physiology Process-based models have been established. The second has been called MATHEMATICIAN and searched for answer to: „How the tree is formed in space ?“ He gave to world: fractal Gift has been accepted in disciplines : formal grammar, fractal geometry, computer graphics Structural models have been established. The third has been called FORESTER and searched for answer to: „What benefit is produced by forest?“ He gave to world: regression equation Gift has been accepted in disciplines : biometry, forest mensuration, forest yield science Empirical models have been established. 1 2 3 2 1 3 1
‘But nothing is so easy in the story as looks at its beginning’ Chessboard of the models 2
static vegetation models (biome models), • (2) eco-physiological tree models, • (3) functional-structural tree models, • (4) empirical distance-dependent tree models, • (5) empirical distance-independent tree models, • (6) tree patch or gap models, • (7) frequency patch or gap models, • (8) frequency population models, • (9) population and species models, • (10) models of functional types, • (11) models of the dynamic of patch or gap groups, • (12) "big leaf" eco-physiological models, • (13) eco-physiological models of the average tree. BALANCE GroIMP SIBYLA 3
Some other frequent types: Biome model 4
Some other frequent types: Gap model 5
Some other frequent types: Big leaf model 6
spatial level biome community population organism organ time level cell second day year decade century millennium 7
Structural downscale SIBYLA - GroIMP biometrical growth morphological growth SIBYLA GroIMP 9
Structural downscale SIBYLA - GroIMP 10
Forest Ecosystem Analysis And Modelling remote sensing knowledge -based and expert systems Computer Aided Forest Modelling geographic information systems aerial laser scanning spatial decision -support systems MSFM high-performance computing forest models AFM terrain measurements PR database systems terrestrial laser skanning virtual reality strategic games internet