Motion
450 likes | 683 Vues
Slow projectile - shoot a monkey. Fast projectile - shoot a monkey. Motion. Objectives. You will be able to explain: Motion Distance Speed Velocity. Motion. Motion - when an objects distance from another object is changing Reference point- place used as a comparison to determine motion.

Motion
E N D
Presentation Transcript
Slow projectile - shoot a monkey Fast projectile - shoot a monkey Motion
Objectives • You will be able to explain: • Motion • Distance • Speed • Velocity
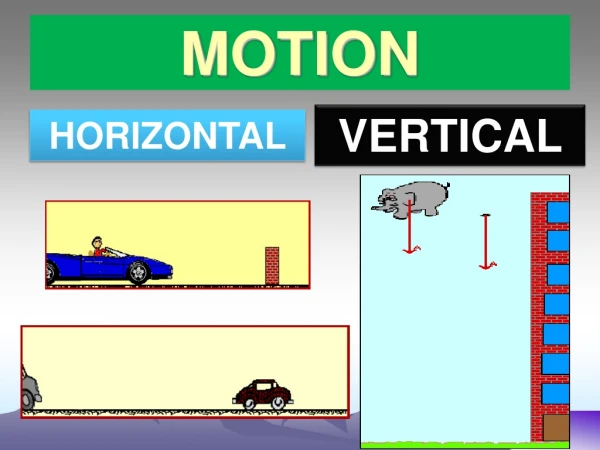
Motion • Motion- when an objects distance from another object is changing • Reference point- place used as a comparison to determine motion
Distance • Distance- always measured using the metric system • Kilometers, meters, centimeters, millimeters
Speed • Speed- the distance an object travels per unit time • Speed=Distance/Time
Speed Lab • Speed= M/Second • 1 meter per second = 2.23693629 miles per hour
Baseball Pitch • The pitchers mound is 60’ 6” from home plate. This is equal to 18.39 M. • If it takes a pitch 1 second to get to home plate, how fast was the pitch? • Remember 1 meter per second = 2.23693629 miles per hour • Answer=
Speed • Speedsters
Speed In Science and Sports • NdamukongSuh
Velocity • Velocity is speed in a direction. • V=D/T
Velocity • Velocity is a vector quantity that refers to "the rate at which an object changes its position." Imagine a person moving rapidly - one step forward and one step back - always returning to the original starting position. While this might result in a frenzy of activity, it would result in a zero velocity. Because the person always returns to the original position, the motion would never result in a change in position. Since velocity is defined as the rate at which the position changes, this motion results in zero velocity. If a person in motion wishes to maximize their velocity, then that person must make every effort to maximize the amount that they are displaced from their original position. Every step must go into moving that person further from where he or she started. For certain, the person should never change directions and begin to return to the starting position.
Review • Ben Roethlisberger can throw a football 60 yards in 4 seconds. How many ft/ second is that? • If there are 5,280 ft per mile, how fast is Big Bens pass in mph? • A bullet from a sniper rifle can travel 5,760 ft/ second. How many miles/ hr is that? How far would it travel in 10 seconds? 3927mph • If a train travels 275 miles in in 5 hours, what is its average speed? What is its velocity? • If I throw a boomerang out at a40 mph and it returns at a speed of 40 mph, what is its average speed? What was its velocity?
Motion Newton's Three Laws
Acceleration • A=(End V - Start V)/time
Force • Newtons Second Law- Force • Force- the product of an objects acceleration and mass Measured in Newtons • Force = Mass x Acceleration • You can rearrange the formula to find acceleration or mass if needed • Acceleration = Force/Mass
Force in sports • Force in sports video
Force Problems • A 52 kg water skier is being pulled by a speedboat. The force causes them to accelerate at 2 m/s. Calculate the net force that causes this acceleration. • What is the net force of a 1000 kg elevator accelerating at 2 m/s? • What net force is needed to accelerate a 55 kg cart at 15 m/s?
Force Continued • How can I increase the force of a football players tackle? • How can I increase the force of a paintball to increase its range?
Friction • Friction- the force that two substances exert as they rub past each other • Lets burn something old school style!!! Stick fire
Friction • There are three types of friction • Sliding friction-when solid surfaces slide over one another • Rolling friction-when an object rolls over another object • Fluid friction-when an object moves through a liquid or gas
Friction • Phonebook Friction • Meter Stick friction demo • Take a meter stick and slide your hands towards oneanother and notice where they meet. • Now start one 50% closer to the middle of the stick and notice where they meet. • Why?
Friction Lab • Do you think that a quarter, dime, or nickel will fall more quickly? • Place a quarter, dime, and nickel at the edge of your desk. • Put a ruler behind them so they can be pushed off evenly. • Push all three over the edge at the same time. • What was the result?
Bell Ringer • List an example of the three types of friction. • How does friction affect force? • What is often a byproduct of friction?
Gravity • Gravity- the force of two objects pulling towards each other • 9.8 m/s2 • So each second an object falls its velocity increases by this rate until terminal velocity is reached. • Air resistance has an effect on gravity • Killer Penny
Gravity • Bullet Drop vs. Shot • Notice the math these guys do. Proof that math is cool. • Lets look at the book pg. 58
Terminal Velocity An object can only fall so fast. At some point it reaches what is known as TERMINAL VELOCITY When air resistance = Gravity For a human this is at about 53m/ S2 or 120mph
Gravity Questions • Calculate your velocity if you jumped from an airplane and fell for 11 seconds. Gravity= 9.8 m/S2 Calculate your velocity if you jump from a swing at 10 ft. Conversion-
Motion Graphing • Objectives • Use Proper Scale • Determine X & Y axis labels • Determine speed, acceleration, and velocity by using graphs
Newton's Third Law • If an object exerts force on another object, the second object exerts the same force in the opposite direction. • So what does that mean? • It means if you and a friend stand on an icy surface and one of you pushes the other you both move equal distances
Momentum • Momentum- is the quantity of motion • Momentum = Mass X Velocity
Momentum Problems • Which has more momentum: • A 3 kg sledgehammer swung at 1.5 m/s or a 4 kg sledgehammer swung at .9 m/s? • A 90 kg hockey player skating at 10 ft/s or a 75 kg player skating at 17 ft/s • A 142 gram baseball going 95 mph or a 190 gram softball traveling 74 mph?
Forces in fluids • Pressure- • Pascal- • Fluid- • Pascal’s Principle- • Hydraulic system- • Buoyant force- • Archimedes Principle- • Density- • Bernoulli’s principle-
Building a Glider • You and your team will have one week to build a glider from Styrofoam. The goal will be the longest flight from my rescue window. You will receive one full class period the day before the flight and 10 min. of each class period up until the flight. The tools for this assignment will be : • Foam • Glue • Paper clips • Bernoulli’s Principle
Pressure • Pressure = Force/Area • Measured in Pascal's (Pa) 1N/M2 =1Pa Or N/cm2 for smaller units
Snow Shoes and Surface area • Book pg. 78
Air Pressure • The air around us exerts pressure on our body. • Why don't we get crushed? • Air pressure at sea level =10.13N/cm2 • More often we use a more common measure of air pressure (mmHg) • 1 mm Hg = 133.322368 Pascal's • 760 mm Hg is the standard air pressure at sea level. This is known as Barometric pressure
Pressure at Elevation • Air pressure is less at elevation. So, water boils espier because the molecules are freed more easily. • What affect does this have on cooking times? • Soda Can • 55 Gallon Drum
Pressure at Depth • As you go deeper the pressure increases. • Pg. 83 • Water Bottle
Buoyancy • Buoyant force- force that works against gravity to keep things afloat • Sinking- when gravity has more force than buoyancy • Floating when buoyancy equals or is greater than gravity • Archimedes Principle- the buoyant force of an object is equal to the weight of water that object displaces
Density • Density= mass/volume • Density determines weather or not something will float
Review of density • If I have a block that is ten cm long by 20 cm wide by 30 cm deep, and its mass is 1000 g, what is its density? • What is the density of a liquid that fills a 100 ml beaker and weighs 100 grams? What liquid would this most likely be? • If a wooden block has a density of 2 g/cm3 will it float or sink?
Bernoulli’s Principle • The faster a fluid moves the less pressure it exerts. • This is why a plain can fly.