Root Canal “System”
70 likes | 354 Vues
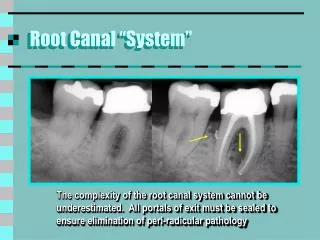
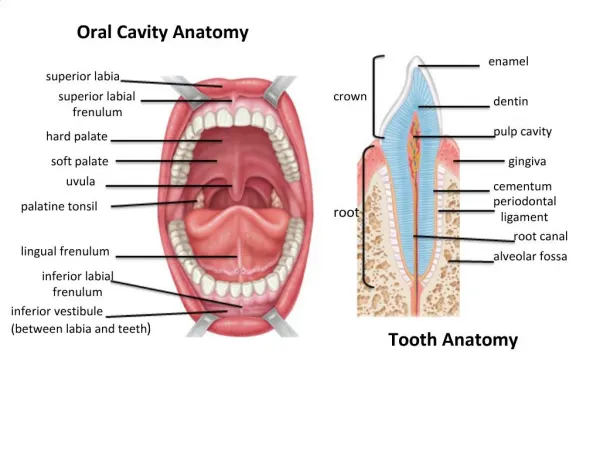
Root Canal “System”. The complexity of the root canal system cannot be underestimated. All portals of exit must be sealed to ensure elimination of peri-radicular pathology. Reengineering. Flexipost cemented in palatal canal – removed with ultrasonic tip

Root Canal “System”
E N D
Presentation Transcript
Root Canal “System” The complexity of the root canal system cannot be underestimated. All portals of exit must be sealed to ensure elimination of peri-radicular pathology
Reengineering • Flexipost cemented in palatal canal – removed with ultrasonic tip • MB2 orifice not identified during previous procedure • contaminants evident in all canals
Reengineering • post removed – all canals identified and negotiated • Class I inlay preparation initiated for NiTi file accessibility and straight line access • heated NaOCl (150o F) and EDTA left to soak in chamber and canal system throughout procedure
Reengineering • canals shaped, cleaned and obturated • gutta-percha sealing to level of orifice interface with chamber floor • bristle brush and ethanol used to remove sealer from chamber • chamber then etched with phosphoric acid in preparation for sealing of the chamber floor and canal orifices
Reengineering • dentinal adhesive (PQ1) used in conjunction with Permaflo to create bonded composite layer over the canal entrances to the root canal system as well as close any furcal canals • further layering of core material can be applied after micro-etching chamber surface • bonded core depth is sufficient to preclude need for post placement
Reengineering • fracture of the mesial-buccal root became apparent on resection – common with amalgam retrogrades not placed with ultrasonics • distal-buccal apex was weakened by original retro-preparation and resection to stable surface shortened root and precluded predictability of trisection
Reengineering The unexpected loss of the tooth is unfortunate for the patient, however, it does demonstrate how the biologic imperative is the foundation for all we do.