Exploring the World of Parallel Architectures: Building Efficient Machines for Solving Complex Problems
80 likes | 194 Vues
Dive into the realm of parallel architectures to understand how building parallel machines can improve speed, cost, accuracy, and solve crucial problems. Learn about the requirements, examples, and pitfalls associated with designing these advanced systems.

Exploring the World of Parallel Architectures: Building Efficient Machines for Solving Complex Problems
E N D
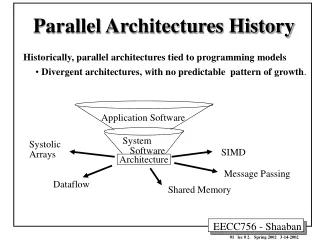
Presentation Transcript
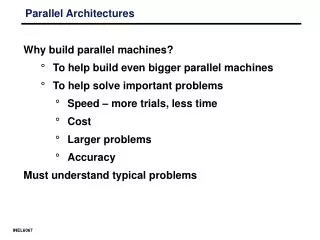
Parallel Architectures • Why build parallel machines? • To help build even bigger parallel machines • To help solve important problems • Speed – more trials, less time • Cost • Larger problems • Accuracy • Must understand typical problems
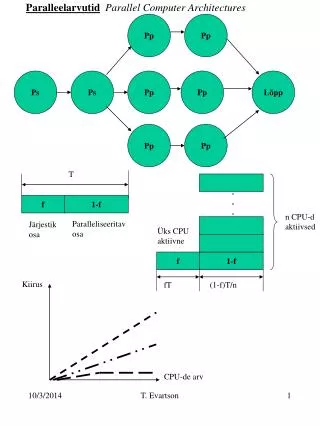
Introduction • A parallel computer is “a collection of processing elements that communicate and cooperate to solve large problems fast” Speedup(p processors)=performance (p processors)/performance (1 processor) Speedup(p processors)=time(p processors)/time(1 processor)
Can run a single parallel application • Speed up the application • Can run multiple independent applications in multiprogramming environment • High throughput • Combination of the two
Numeric Symbolic Combinatorial Applications ---> Requirements • Processing • Communication • Memory • I/O • Synchronization • Architect must provide all of the above
Requirements ---> Examples • Relaxation - near-neighbor communication • Multigrid - 1, 2, 4, 8, ... communication • Numeric comp - Floating point • Symbolic - Tags, branches • Database - I/O • Data parallel - Barrier synchronicity • Dictionary - Memory, I/O
Communication requirements ---> Example • Relaxation • So, let’s build a special machine! • But ... pitfalls!
Specialized machines: Pitfalls • Faster algorithms appear … with different communication requirements • Cost effectiveness • Economies of scale • Simpler hardware & software mechanisms • More flexible • May even be faster! • e.g. Specialized support for synchronization across multiple processors