Fate of Cells
70 likes | 527 Vues
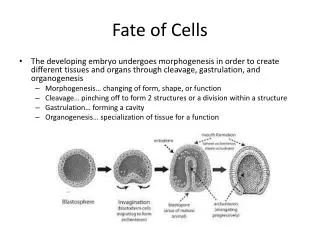
Fate of Cells. The developing embryo undergoes morphogenesis in order to create different tissues and organs through cleavage, gastrulation, and organogenesis Morphogenesis… changing of form, shape, or function Cleavage… pinching off to form 2 structures or a division within a structure

Fate of Cells
E N D
Presentation Transcript
Fate of Cells • The developing embryo undergoes morphogenesis in order to create different tissues and organs through cleavage, gastrulation, and organogenesis • Morphogenesis… changing of form, shape, or function • Cleavage… pinching off to form 2 structures or a division within a structure • Gastrulation… forming a cavity • Organogenesis… specialization of tissue for a function
Cell Differentiation • Cells are totipotent in the first 16 cells of the of the blastocyst • Potency is reduced with each cell specialization there after • Initial differentiation due largely to uneven distribution of cytoplasmic determinants in the yolk of the egg • Egg is polarized creating heterogeneous cytoplasm • Cleavage creates uneven distribution of mRNA and asymmetrical cell division • Process of induction causes the specialization of most cells • Created through contact via diffusible chemical signals
Fate Mapping • Manipulation of embryonic cells to determine the lineage of cells from the first cleavage event
Cellular Asymmetries • Axes of body plan • Anterior-posterior, ventral-dorsal, right-left • Establishes bilateral symmetry • 1st step in morphogenesis and tissue/organ formation • Bicoid region of flies • Determined by melanin in the yolk during oogenesis • Gravity helps determine anterior/posterior axis in chicks • pH determines ventral/dorsal…marked by the gray crescent in many embryos