Radioactive Decay
160 likes | 301 Vues
This guide explores the fundamental concepts of radioactive decay, detailing the various types of nuclear radiation, including alpha particles, beta particles, gamma rays, and neutron emission. It defines isotopes and their relationship to neutron counts, illustrating how isotopes affect atomic characteristics. The importance of half-lives, which indicate the decay rate of isotopes, is also discussed, providing practical examples such as radium-226 and uranium-238. This concise overview is essential for understanding radiation in everyday life and nuclear processes.

Radioactive Decay
E N D
Presentation Transcript
Radioactive Decay Read pages 191-196 157
Atoms are held together by The strong nuclear force
There are different types ofnuclear radiation • Alpha particles • Beta particles • Gamma rays • Neutron emission
Alpha particles • Positively charged • More massive than other types • Released in the disintegration of radioactive elements • Consists of two protons and two neutrons A helium nucleus , which carries a charge of . http://library.thinkquest.org/3471/radiation_types_body.html
Beta particle • A charged electron emitted during certain types of radioactive decay • Neutrons decay to form a proton and a high speed electron • The electron is ejected
Neutron emission • is a type of radioactive decay of atoms containing excess neutrons, in which a neutron is simply ejected from the nucleus.
Gamma rays • High energy photon emitted by a nucleus during fission and radioactive decay
What stops it? • Alpha • Beta • Gamma
Isotope • An atom with a different number of neutrons is called an isotopeHydrogen usually is a proton and an electronIf it has a neutron it is considered an isotopeHydrogen deuterium tritium 0 neutrons 1 neutron 2 neutrons
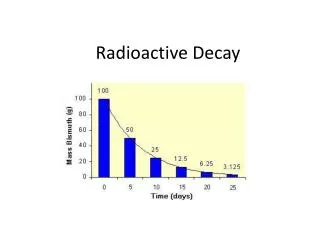
Half-lives • The rate of decay of an isotope is called the half-life.A half life is the amount of time it takes for half of the amount to decay.It is constant • Different elements have different half-livesRadium-226=1620 yearsUranium-238 = 4.5 billion years
158 200g radium -226 half-life of 1620years100g 162050g 3240_____g 486012.5g _______6.25g 8100________g 97201.5625g _______
Table Design Make a table for Table 1 problems!
Periodic Table Practice Lithium 7 Li 3 3P 4N mass Mass=p + n Atomic symbol Atomic number Neutrons = mass - protons
REMEMBER—this is all about isotopes • Atomic number = # of protons • You absolutely must figure your own mass or number of neutrons • Don’t use the chart • Mass = protons + neutrons • Neutrons = Mass – protons