Cell Structure & Function
250 likes | 920 Vues
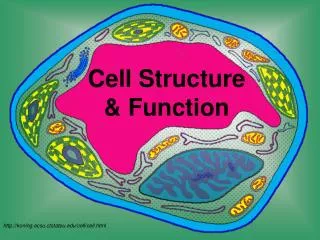
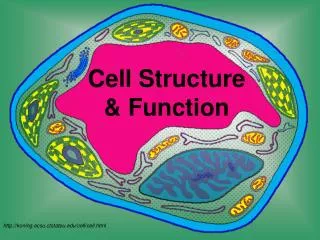
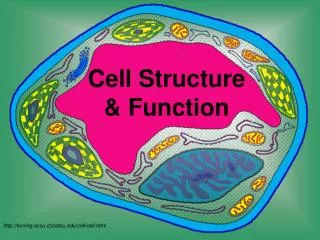
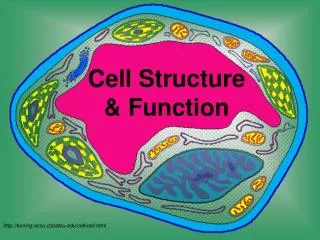
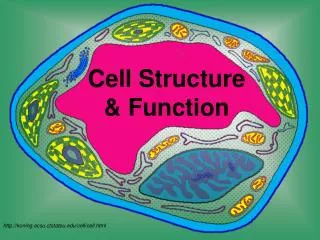
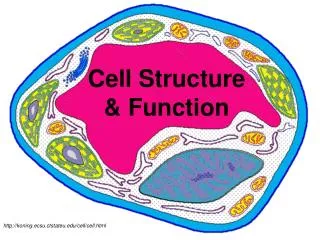
Cell Structure & Function. http://koning.ecsu.ctstateu.edu/cell/cell.html. Definition of Cell. A cell is the smallest unit that is capable of performing life functions. Examples of Cells. Amoeba. Plant Cell. Red Blood Cell. Nerve Cell. Organelles .

Cell Structure & Function
E N D
Presentation Transcript
Cell Structure & Function http://koning.ecsu.ctstateu.edu/cell/cell.html
Definition of Cell A cell is the smallest unit that is capable of performing life functions.
Examples of Cells Amoeba Plant Cell Red Blood Cell Nerve Cell
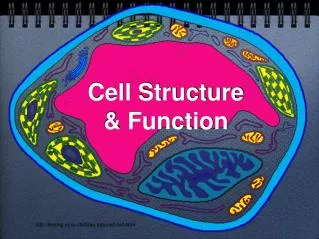
Organelles • Organelles are the parts of the cell that perform different functions. • There are 11 main organelles (9 for animal cells)
“Typical” Animal Cell http://web.jjay.cuny.edu/~acarpi/NSC/images/cell.gif
“Typical” Plant Cell http://waynesword.palomar.edu/images/plant3.gif
Cell Parts Organelles
Cell Wall • Gives shape and support to cell • Plants and protists, like algae, have cell walls • Fungi, like yeasts and mushrooms, also have cell walls • Bacteria and Archae also have cell walls, but they are different from plant and fungi • Animal cells DO NOT have cell walls
Cell Membrane • “Gatekeeper” of the cell that controls what can come in or out of the cell • Semi-permeable
Nucleus • Controls the cell’s activities • It’s like the “boss” or the “brains” of the cell • DNA is found inside the nucleus
Nuclear Membrane • The “gatekeeper” of the nucleus • Protects the outside of the nucleus • Controls what can go in or out of the nucleus
Chromosomes • Long pieces of DNA inside the nucleus • Come in pairs-one from your mom and one from your dad • Humans have 23 pairs of chromosomes, 46 total chromosomes
Cytoplasm • Soupy, Jell-O like substance that holds all organelles inside the cell in place
Ribosomes • Each cell contains thousands • Make proteins for the cell
Mitochondria • Makes energy (ATP) by breaking down fats and carbohydrates • Controls level of water and other materials in cell • If your mitochondria wasn’t working properly, you wouldn’t be making enough energy and may feel very tired!!
Lysosomes • Digest proteins, fats, and carbohydrates • Clean up cell’s waste by sending them to the cell membrane for disposal
Vacuoles • Storage centers for both plant and animal cells • Much larger in plant cells because of the storage of water • Gives plant cells shape (along with cell wall)
Chloroplast • ONLY found in plant cells • Contains chlorophyll, which is where plants get their green pigment • Where photosynthesis takes place
Cell Membrane Cell Wall Chloroplasts Mitochondria Ribosomes Lysosomes Vacuole Chromosomes Nucleus Nuclear Membrane Cytoplasm Controls what goes in/out of nucleus Controls cell activities Creates proteins for cell Contains/long pieces of DNA Gives the cell shape and support Controls what goes in/out of cell Contains chlorophyll for photosynthesis Storage of food and water Gobbles up the waste Jell-O like substance that holds parts in place Produces energy for the cell Match That Part!
How to Write an Analogy • An analogy is a comparison between two seemingly unlike things, using the words like or as and giving an explanation. • For example: -The nucleus is to a cell as Mrs. Opferman is to Webb Bridge Middle School • Now you practice will cell parts! • The nucleus is to a cell as _______is to a ________________.
Animal Both Plant