CARTILAGE
370 likes | 1.03k Vues
CARTILAGE. By Dr Iram Tassaduq. CARTILAGE. Is a specialized type of connective tissue. Form part of skeleton where flexibility is required Does not contain vessels or nerves. . COMPONENTS OF CARTILAGE. Consists of cells and extracellular components. Does not contain vessels or nerves.

CARTILAGE
E N D
Presentation Transcript
CARTILAGE By Dr Iram Tassaduq
CARTILAGE • Is a specialized type of connective tissue. • Form part of skeleton where flexibility is required • Does not contain vessels or nerves.
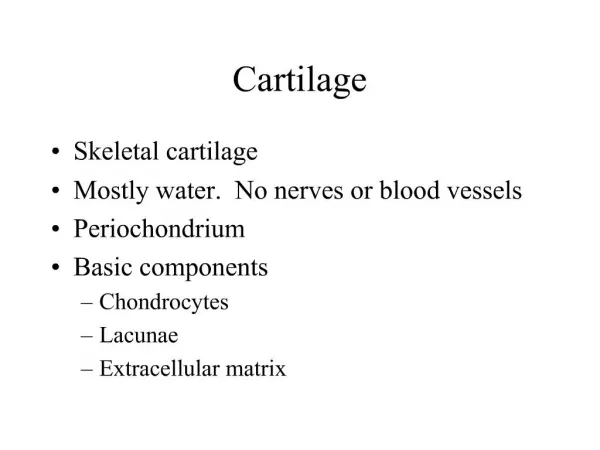
COMPONENTS OF CARTILAGE • Consists of cells and extracellular components. • Does not contain vessels or nerves. • Is surrounded by a layer of dense connective tissue, the perichondrium
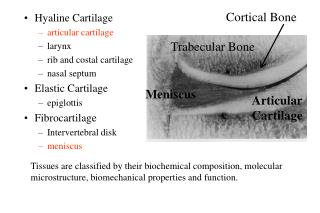
TYPES OF CARTILAGE • Hyaline cartilage • Elastic cartilage • Fibrous cartilage
FUNCTIONS OF CARTILAGE • Firm consistency of the extracellular matrix allows the tissue to bear mechanical stresses without permanent distortion • Supports soft tissues. • Shock-absorbing because it is resilient. • Smooth surface allows sliding . • Essential for growth, development of bone.
CHARACTERISTICS • Chondrocytes • Located in lacunae • Extensive extra-cellular matrix • Fibers, Collagen, &elastic • Ground substance • Fibers bind together and give firm, flexible properties to tissue
CHONDROCYTES • Produce and maintain extra cellular matrix. • Either single or in isogenous groups . • Fat droplets, glycogen granules are found in cytoplasm. • Active ones are more basophilic.
PERICHONDRIUM • Dense CT that covers cartilage • Contains blood, nerve supply, lymphatics. • Source of new cartilage cells • Divided into two layers Inner cellular Outer fibrous
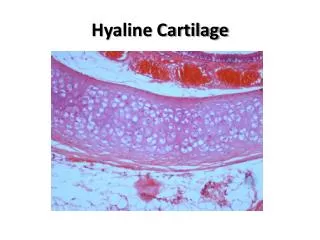
HYALINE CARTILAGE • Fundamental type and most common • Occurrence: • Ribs (ventral ends) • Long bones (articular surfaces) • Nose, Larynx, Trachea, Bronchi • Fetal skeleton (except membrane bones)
CLASSIFICATION OF HYALINE CARTILAGE Articular Costal Epiphyseal
HYALINE CARTILAGE • Cells embedded in clear matrix • Perichondrium on surface
Found at ends of bones, • nose, trachea, larynx • Bluish white color. • Strong, rubbery, flexible tissue.
EXTRA CELLULAR MATRIX • The matrix near the isogenous groups of chondrocytes is termed territorial matrix or capsule. In H&E stained sections the territorial matrix is more basophilic, i.e. it stains darker. • The remainder of the matrix is called the interterritorial matrix.
ARTICULAR CARTILAGE • Hyaline cartilage of articular surfaces do not posses a perichondrium
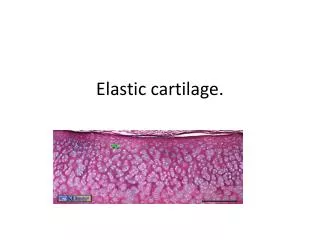
ELASTIC CARTILAGE • Similar to hyaline cartilage but has elastic fibers running in all directions in addition to collagen.
ELASTIC CARTILAGE Found in auricle of ear, walls of external auditory canals, eustachian tubes, epiglottis, larynx Maintains shape, deforms but returns to shape; flexibility of organ; strengths and supports structures.
FIBROCARTILAGE • Chondrocytes may lie singly or in pairs, but most often they form short rows between dense bundles of collagen fibres.
FIBROCARTILAGE • Collagen type I is dominant in fibrous cartilage • is typically found in relation to joints (forming intra-articulardisks and menisci) intervertebral disks, symphysis pubis.