Advances in Medical Imaging Technologies and Detector Development
270 likes | 376 Vues
Explore the evolution and benefits of digital medical imaging over conventional methods, including diverse modalities such as CT, MRI, PET, SPECT, and more. Learn about detector advancements, image processing, PACS, and future opportunities for enhancing diagnostic capabilities.

Advances in Medical Imaging Technologies and Detector Development
E N D
Presentation Transcript
Medical Imaging A review of medical imaging technologies with some opportunities for detector development
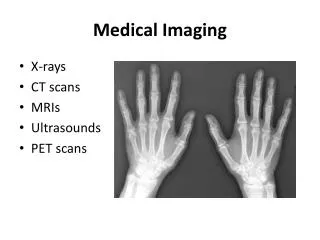
Medical Imaging • Intrinsically Digital - CT, MRI, Angiography/Fluoroscopy, Ultrasound, Gamma Camera, PET, SPECT • Analogue - Radiography (X-rays) - accounts for 70% of all clinical images • Digital X-ray - computed radiography, direct digital radiography (a:Si, a:Se, CCD, CMOS) • Radionuclide imaging: gamma camera, PET, SPECT • Digital advantages - CAD, digital processing, teleradiology
Picture Archiving and Communications Systems (PACS) • Most large hospitals in developed world are installing PACS • Digital capture and storage of medical images • Standardised communications and image format • Large archive accessible from Dr’s clinics, wards, theatres, etc • Teleradiology gives access to specialists in other hospital/country • Do away with film library, waiting times and lost films
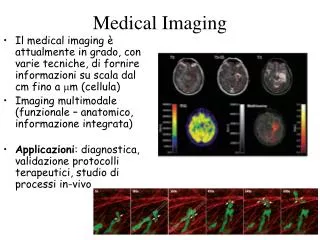
Radiology Images Chest CT Head MRI Pancreatic Fluoro Pelvic Angiograph Renal US Chest X-ray
Nuclear Medicine Images PET Gamma Camera SPECT
Screen/Film Imaging The first X-ray image dates from 1895, and plane film technology has continued to dominate medical imaging for over 100 years Mrs Wilhelm Roentgen’s hand
Film / Digital Response to Exposure Film provides an inherent logarithmic compression of exposure onto the available optical densities of the film but has a limited dynamic range Digital detectors give a linear response to exposure so must have logarithmic processing, also gives a much larger dynamic range
Computed and Direct Radiography Direct - TFT, CCD, CMOS Computed Radiography • Photostimulable phosphor plates • Cheap • Flexibility of plates for mobile X-rays • Plates can be used on existing X-ray machines • TFT - Amorphous Si, Se • More sensitive than CR • Faster imaging process/workflow • Enables real-time processing • Dual energy imaging • Video fluoroscopy - if frame rates permit
Computed Radiography Workflow is similar to screen/film process: 1. Latent image formation on photostimulable phosphor CR plate 2. Plate is read by scanning laser 3. Digital image is processed and archived Conventionalscreen/film Computed Radiography
Advantages of CR • Flexibility: • Plates are portable and ‘cheap’ • Plates work with existing X-ray equipment • CR can be used for most exams - mammography being one exception • Hospitals can translate to a digital environment without buying new X-ray equipment • Archives and viewing workstations are established • Other digital modalities can now be considered
Flat Panel TFT Detectors Indirect: a-Si Direct: s-Se
Flat Panel Detector Expensive Not portable Pixel size ~ 100 m Efficient - lower dose Improves throughput in dedicated rooms
Optically Coupled CCD CCD chip is small ~ 2x2cm Pixels are small ~ 12m Large field must be demagnified using fibre-optictaper or lenses - inefficient
CMOS - Medipix 2 55x55 m pixels 1.5x1.5 cm chip size Si, GaAs, CdTe, CdZnTe sensor chip Photon-counting rather than integrating Thresholding Fast
Dose and Energy ALARA - As Low As Reasonably Achievable Lower energies give greater absorbed dose Different tissues are more susceptible to damage, eg glandular breast tissue Diagnostic Energy Range: 120kV for a chest X-ray, to maximise latitude in bone and soft lung-tissue imaging 25kV for mammography to maximise contrast in the soft tissues of the breast
Digital Mammography • Small calcifications require 20 line pairs/mm • Glandular tissue more sensitive to radiation • Higher doses needed, repeated imaging also increases dose • Due to coupling inefficiencies, higher dose than film • 11 lp/mm not as good as film
Stereotactic Biopsy Mammography • Biopsy of suspect lesion in the breast to determine malignancy • The breast is clamped and imaged from two angles to determine location of tumour • Computer calculates needle insertion point and path • Dramatically decreases the time of the procedure with increased patient comfort and cost effectiveness • Smaller imaging field - 5x5cm
Fluoroscopy • Video plane radiography, gives live view of internal motion and function • Photocathode/anode acceleration gives amplification of image • Video needs frame rate of ~ 30fps • a:Si flat panels have been used - reads 30 million pixels/s (a:Se too slow)
Nuclear Medicine Imaging CdZnTe detectors have found applications in gamma cameras, where they replace the scintillator and PMT Surgical gamma probe - 140keV from 99TcMedipix (Bertolucci et al, 2002) - 2mm think CdZnTe for high efficiency Sentinal Lymph Node Biopsy- to establish progression of breast cancer - intraoperative probe provides 1mm resolution of the node location for biopsy
PET Scan • Detectors are scintillation crystals coupled to PMTs • Decay constant of BGO ~ 300nsec • Faster detectors improve discrimination of coincidence • Very fast detectors time of flight calculations and positron imaging Emitted positron travels short distance from nucleus before annihilation with electron, producing two 511 keV photons
Dual Energy Imaging Bone Image Soft Tissue Image
Digital Tomosynthesis Image Stitching
Medipix Wish List • Large area tiled detector - 45x30cm • Fast readout - 107 pixels in 1/30 sec • Sensitive from 20 to 400keV • Efficient - reduce dose, enable fluoroscopy • Feedback circuit to control X-ray tube and cut off when sufficient image info is captured? • Research projects for Medical Physics MSc students