Guidelines for Selecting Appropriate Statistical Methods for Data Analysis
40 likes | 143 Vues
This document provides a comprehensive guide for selecting the appropriate statistical methods based on the type of data (nominal, ordinal, interval, or ratio) and the specific analysis objectives. It covers how to choose descriptive statistics such as mean, median, and mode, as well as parametric and nonparametric statistics for evaluating group differences. Additionally, it examines the relationship between two variables using linear and monotonic methods, providing criteria for matched and independent samples. This tool is essential for researchers and analysts to ensure valid interpretations of their findings.

Guidelines for Selecting Appropriate Statistical Methods for Data Analysis
E N D
Presentation Transcript
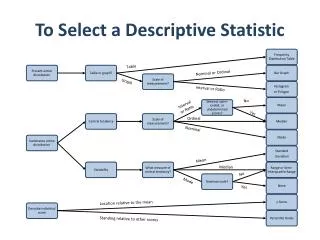
To Select a Descriptive Statistic Table Nominal or Ordinal Graph Interval or Ratio No Interval or Ratio Yes Ordinal Nominal Mean Median No Mode Yes Location relative to the mean Standing relative to other scores
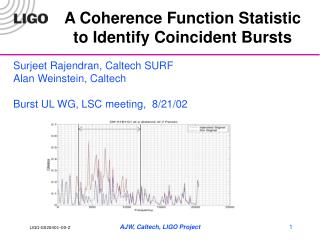
To Select a Statistic to Measure theRelationship Between Two Variables Linear Yes Monotonic Yes None No No Only one Two
To Select a Parametric Statisticto Evaluate Group Differences Yes No One Two More than two One Matched Two Independent More than two Matched One Independent Two
To Select a Nonparametric Statisticto Evaluate Group Differences Two or more One Only two No Two One Yes Matched Two Yes Independent No No More than two Discrete Continuous