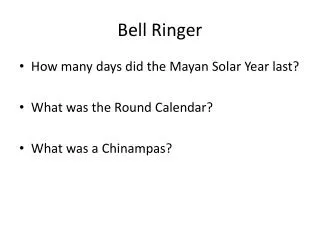Bell Ringer
110 likes | 222 Vues
This lesson covers the definitions and properties of rhombuses, squares, and rectangles, which are all types of parallelograms. A rhombus has four congruent sides and specific angle and diagonal properties. A square is a rhombus with four right angles, while a rectangle has four right angles and congruent diagonals. The lesson includes examples and problems related to these shapes, helping students apply their understanding of properties, relationships, and calculations involving angles, sides, and diagonals.

Bell Ringer
E N D
Presentation Transcript
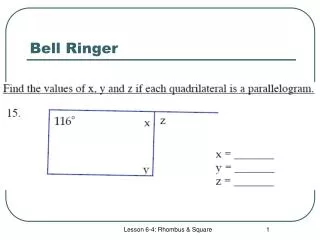
Bell Ringer Lesson 6-4: Rhombus & Square
Rhombi Rectangles & Squares
Rhombus Definition: A rhombus is a parallelogram with four congruent sides. • Opposite sides are parallel. • Opposite sides are congruent. • Opposite angles are congruent. • Consecutive angles are supplementary. • Diagonals bisect each other ≡ ≡ Since a rhombus is a parallelogram the following are true:
Properties of a Rhombus Theorem: The diagonals of a rhombus are perpendicular. Theorem: Each diagonal of a rhombus bisects a pair of opposite angles.
Rhombus Examples ..... Given: ABCD is a rhombus. Complete the following. • If AB = 9, then AD = ______. • If m<1 = 65, the m<2 = _____. • m<3 = ______. • If m<ADC = 80, the m<DAB = ______. • If m<1 = 3x -7 and m<2 = 2x +3, then x = _____. 9 units 65° 90° 100° 10
Square Definition: A square is a parallelogram with four congruent angles and four congruent sides. • Opposite sides are parallel. • Four right angles. • Four congruent sides. • Consecutive angles are supplementary. • Diagonals are congruent. • Diagonals bisect each other. • Diagonals are perpendicular. • Each diagonal bisects a pair of opposite angles. Since every square is a parallelogram as well as a rhombus and rectangle, it has all the properties of these quadrilaterals.
Squares – Examples…... Given: ABCD is a square. Complete the following. • If AB = 10, then AD = _____ and DC = _____. • If CE = 5, then DE = _____. • m<ABC = _____. • m<ACD = _____. • m<AED = _____. 10 units 10 units 5 units 90° 45° 90°
Rectangles Definition: A rectangle is a parallelogram with four right angles. • Opposite sides are parallel. • Opposite sides are congruent. • Opposite angles are congruent. • Consecutive angles are supplementary. • Diagonals bisect each other. A rectangle is a special type of parallelogram. Thus a rectangle has all the properties of a parallelogram.
A B E D C Properties of Rectangles Theorem: If a parallelogram is a rectangle, then its diagonals are congruent. Therefore, ∆AEB, ∆BEC, ∆CED, and ∆AED are isosceles triangles. Converse: If the diagonals of a parallelogram are congruent , then the parallelogram is a rectangle.
A B 2 3 1 E 4 5 6 D C Examples……. • If AE = 3x +2 and BE = 29, find the value of x. • If AC = 21, then BE = _______. • If m<1 = 4x and m<4 = 2x, find the value of x. • If m<2 = 40, find m<1, m<3, m<4, m<5 and m<6. x = 9 units 10.5 units x = 18 units m<1=50, m<3=40, m<4=80, m<5=100, m<6=40