Bell Ringer
220 likes | 365 Vues
Explore the intricacies of Earth's mapping, including the differences between the prime meridian and meridians, and why cardinal directions provide clearer navigation. Dive into cartography, the issues of representing a 3D sphere on 2D surfaces, and the various map projections such as Mercator, conic, gnomic, and Robinson. Learn about modern technologies like remote sensing, GPS, and GIS that enhance our ability to understand and navigate the planet. Discover how distortion affects maps and the importance of features such as scale, legend, and compass rose.

Bell Ringer
E N D
Presentation Transcript
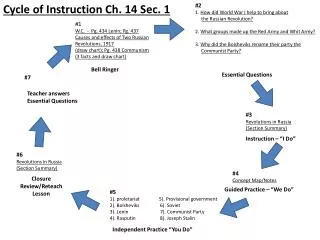
Bell Ringer • Draw a longitude line. • Explain why the prime meridian and meridian are two different lines. • Why does Earth have more than one pole? • Why are cardinal directions a more accurate way of giving directions?
Mapping the Earth’s Surface • Cartography – the science of map making.
Maps are Models of the Earth • A globe is the most accurate model of the Earth because it eliminates distortion.
Mapping the Earth’s Surface • What are some issues with mapping the Earth’s surface on a map? • Trying to put a 3d sphere on a 2d piece of paper • Objects become distorted ex. Iceland
Map Projections • All maps have some sort of distortion. • Maps that show larger areas have more distortion than maps that show a smaller area.
Map Projections • Map projections are based on three different shapes. • Cylinders • Cones • Planes
Mercator Projection • Mercator Projection –a map projection that is made by moving the surface features of the globe onto a cylinder. • Touches the globe at the equator but distance between the map and globe increase as you move up in longitude.
Mercator Projection • Longitude and Latitude are shown as straight lines. • Distance between two points are shorter when using curved lines. • Areas near the poles tend to look larger than objects located along the equator. • Ex. Greenland and Africa http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=cuuluAq4TtU&feature=related
Conic Projection • Conic Projection – a map projection that is made by moving the surface features of the globe onto a cone. • No distortion along the line of latitude where the globe touches the cone. • Used to map larger areas that have more area east to west like the united states.
Gnomic Projection • Gnomic Projection – a map projection that is made by moving the surface features of the globe onto a plane. • Touches the globe at only one point. • Usually is used to map the poles. • Distortion of direction, distance, and shape increases as you move away from the point of contact.
Robinson Projection • Created in 1963 by Arthur Robinson • Latitude projected as straight lines and Longitude are projected as curved lines.
Robinson Projection • Has Less distortion near the poles. • Features within 45 degrees of the equator are closer to their true dimensions. • Distance along each latitude lines are true but the scales change.
Information on Maps • Regardless of the type of map you are using it should include some of the following the more of this information a map has the more accurate it will be.:(pg46) • Title • Compass rose • Scale • Legend • Date
Modern Mapmaking • Remote Sensing – the process of gathering and analyzing information about an object without physically being in touch with the object. • An Example of remote sensing include: • Taking pictures from and Airplane • Sophisticated technology of Satellites
Geostationary Orbit • A type of satellite orbit that takes 24 hours to complete one orbit of the Earth. • Helps to identify changing weather in a geographical location.
Polar Orbit • A satellite orbits the Earth from the North Pole to the South Pole. • Occurs every 90 minutes. • Weather satellites can observe the change in the world weather in 1 day.
Remote sensing using radar • Radar is a tool that uses waves of energy to map earth surfaces. • Waves are sent from a satellite to the area being observed and then sent back to the satellite. • The speed of the light that returns is measured and analyzed to create a picture. • Radar has the ability to move through clouds and water.
Global Positioning System • Global positioning system (GPS) – a system of orbiting satellites that send radio signals to receivers on Earth. • GPS History • Invented in the 1970’s by the U.S. Department of defense for military use. • GPS is now used by boaters, pilots, and car drivers.
Geographic Information Systems • Geographic information System (GIS) – is a computerized system that allows a user to enter different types of information about an area. • This information can then be used to make complex analyses or display maps.