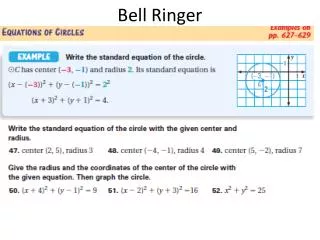
Bell Ringer
110 likes | 229 Vues
This lesson focuses on determining the slopes of line segments RS and TS formed by given points R, S, and T. Learners will calculate the slopes and investigate whether these segments are perpendicular. Additionally, students will explore the properties of polygons, including the sums of interior and exterior angles. Through collaborative exercises like Rally Coach and Rally Robin, students engage in problem-solving and sharing knowledge about various polygons, culminating in the analysis of a benzene molecule's structure and its significance in chemistry.

Bell Ringer
E N D
Presentation Transcript
Bell Ringer Find the slopes of RS and TS for the given points, R, T, and S. Determine whether RS and TS are perpendicular or not perpendicular. R(4,5), S(-1,10), T(13,20)
Rally Coach • Partners take turns, one solving a problem while the other coaches. • 1. Partner A solves the first problem. • 2. Partner B watches and listens, checks, coaches if necessary, and praises. • 3. Partner B solves the next problem. • 4. Partner A watches and listens, checks, coaches if necessary, and praises.
Rally Coach • Find the slopes of RS and TS for the given points, R, T, and S. Determine whether RS and TS are perpendicular or not perpendicular. • R(-9,6), S(3,8). T(1,20) • R(-6,-1), S(5,3), T(2,5)
Geometry SLE • R.4.G.2 • Objective: I will find the sum of the measures of the interior and exterior angles of polygons. I will also find the measure of each interior and exterior angle when the sides and angles are all congruent, which is called a regular polygon.
Write Rally Robin • Students take turns stating and writing responses or solutions. Record answers on one sheet of paper.
Name as many polygons as you can think of and record your answers on your sheet of paper.
Benzene Molecule The benzene molecule C6H6, consists of six carbon atoms in a regular hexagonal pattern with a hydrogen atom attached to each carbon atom. Find the sum of the measures of the interior angles of the hexagon. The chemical compound benzene (C6H6) is a colorless, flammable, aromatic hydrocarbon, that is a known carcinogen. It boils at 80.1°C and melts at 5.5°C. Benzene has a heat of vaporization of 44.3 kJ/mol and a heat of fusion of 9.84 kJ/mol. Produced by hydrogen reduction of some allotropes of carbon, or from petroleum, it is used in the creation of drugs, plastics, gasoline, synthetic rubber, napalm and dyes.