Overview of Emission-Free Energy Sources in the U.S. and Nuclear Power's Future
50 likes | 169 Vues
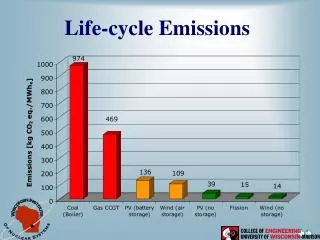
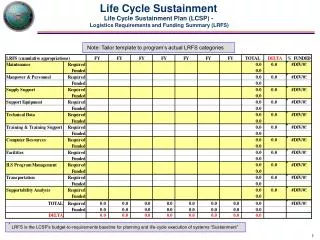
This document analyzes the life-cycle emissions associated with various sources of emission-free electricity generation in the United States. Geothermal contributes 1.3%, photovoltaics less than 1%, hydroelectric power accounts for 29.1%, wind energy provides 34%, while nuclear power stands out with a remarkable 69.2%. Additionally, the document examines nuclear electricity production trends and cost efficiency from 1998 to 2001, highlighting improved capacity factors and lowest electricity production costs. It aims to provide insights into the role of nuclear energy in the 21st century.

Overview of Emission-Free Energy Sources in the U.S. and Nuclear Power's Future
E N D
Presentation Transcript
Environmental Impact:US Sources of Emission-Free Generation (2009) Geothermal 1.3% Photovoltaic <.1% Hydro 29.1% Wind .34 % Nuclear 69.2% Nuclear Power: Prospects for the 21st Century Source: EIA
Record U.S.Nuclear Electricity Production (Billions of Kilowatt-hours) Source: EIA Nuclear Power: Prospects for the 21st Century
Capacity Factors Improvement 95% 86.8% in 1999 89.6% in 2000 90.7% in 2001 91.7% in 2002 85% 75% 65% 55% ‘80 ‘85 ‘90 ‘95 Source: NEI ‘00 Nuclear Power: Prospects for the 21st Century
Lowest Electricity Production Costs 3.5 2.09 ¢/kWh in 1998 1.90 ¢/kWh in 1999 1.81 ¢/kWh in 2000 1.68 ¢/kWh in 2001 3.0 2.5 (cents/kilowatt-hour) 2.0 1.5 ‘80 ‘85 ‘90 ‘95 ‘00 Source: NEI Nuclear Power: Prospects for the 21st Century