Chapter 31 Reptiles & Birds
360 likes | 982 Vues
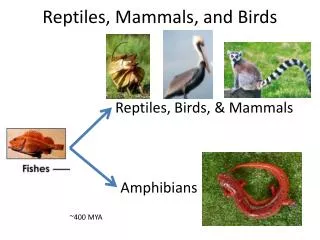
Chapter 31 Reptiles & Birds. Evolution. Dinosaurs are reptiles that walked leg below hip and either had: Bird hips ( Ornithischia ) Lizard hips ( Saurischia ). Hylonomus (hylo- "forest" + nomos "wanderer") earliest known reptile lived 315 MYA - about 12 inches long -.

Chapter 31 Reptiles & Birds
E N D
Presentation Transcript
Evolution • Dinosaurs are reptiles that walked leg below hip and either had: • Bird hips (Ornithischia) • Lizard hips (Saurischia). Hylonomus (hylo- "forest" + nomos "wanderer") earliest known reptile lived 315 MYA - about 12 inches long -
Evolution - Mesozoic Era Earliest known reptile lived 315 MYA / earliest dinosaur 245 MYA
Mesozoic Era 2-7 centimeters a year = 730-2,555cm = 7.3-25.55m
Extinction - 65MYA Adaptive Radiation
Birds • Song Birds • Shore Birds • Birds of Prey • Wading Birds • Sea Birds • Game Birds Reptiles Lizards Snakes Crocodilians Turtles & Tortoises Tuataras - primitive scales, no external ears, third eye Groups of Reptiles & Birds • Amphibians • Toads • Frogs • Salamanders • Mammals • Placental Animals • Marsupials • Monotremes
Evolution Reptile: Dry scaly skin Ectothermic Tetrapods Amniotes – terrestrial eggs • Amphibians • Permeable Moist Skin • Tetrapod • Four Digits Front & Five on Back Limbs • Ectothermic • Mammals • Produce Milk • Have Hair • Lower Jaw Single Bone • Middle Ear 3 Bones • Have a diaphragm • Live birth all but.. • Endothermic Birds: Feathers Endothermic Amniotes
Avian Skeletal Structure Bones 1.Hollow reinforced with struts 2. Fused collar bone 3. Large keeled sternum Amphibians 1. Reduced or No ribs that do not meet the sternum
Feathers Contour Feathers Down -Preening -Molting
Movement • Types of Flight • Straight • Hovering • Soaring • Dive • Swimming • Landing • Take Off
Avian - Respiratory System Air Sacs expand rather than lungs 1. Inhalation - air flows into abdominal and posterior sacs – through lungs 2. Exhalation – air in sacs moves to lungs 3. Inhalation – air in lungs moves to interclavicular, thorasic, & anterior sacs 4. Second Exhalation – air moves out
Reptilian Respiratory System Limited cloacal breathing Lungs are necessary in all reptiles, but filling them is achieved differently. Many reptiles must hold their breath to run as they use the same muscles for breathing and physical effort.
Snake Respiration Bull Snake Trachea Snakes breathe by contracting muscles between their ribs. Unlike mammals, they lack a diaphragm.. Inspiration is an active process (muscles contract), whereas expiration is passive (muscles relax). In most snakes the right lung is usually the largest and extends for over a 1/3 of the body. The left lung is then VERY small or absent.
Snake Digestion During periods of fasting the lining, or mucosa, of the small intestine becomes atrophied, conserving the snake’s energy and resources. Snakes become dormant after large meals and if threatened right after a meal they may regurgitate to escape. Feeding stimulates rapid growth of the intestinal lining and the liver and enters into a period of rapid growth and increased activity.
Digestion Crop - stores & moistens food (crop milk) Gizzard - part of stomach used for grinding hard materials - rocks are often used Stomach Small Intestine Large Intestine
Nictitating Membrane Put in with eye sight Nictitating Membrane