Head Injuries
240 likes | 485 Vues
Head Injuries. Care & Prevention of Athletic Injuries Ms. Herrera ATC/L. Concussion News Clip. Anatomy. Skull is made of 28 bones Joined together by “sutures” (immovable joints) Temporal bone is the thinnest aspect. Anatomy Cont’d. Brain Weighs about 3 lbs

Head Injuries
E N D
Presentation Transcript
Head Injuries Care & Prevention of Athletic Injuries Ms. Herrera ATC/L Concussion News Clip
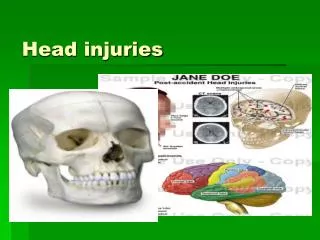
Anatomy • Skull is made of 28 bones • Joined together by “sutures” (immovable joints) • Temporal bone is the thinnest aspect.
Anatomy Cont’d • Brain • Weighs about 3 lbs • Brain cells develop till 18 years old • Once they die they can’t be reproduced • Oxygen leads to brain death • Divided into lobes • Frontal • Parietal • Occipital • Temporal • *each has a specific function
Anatomy Con’td • Brain is attached to the spinal cord via the brain stem • CSF function? • Suspends the brain • Cushions • Lessons forces
General Information • Head injuries occur in… • Contact and collision sports • Examples? • MOI • Direct blow to the head • Impact causing the head to snap in different directions
General Signs & Symptoms • Brain injury may result in… • LOC • Track time of LOC • Unconsciousness happens when brain receives too many signals and becomes overwhelmed • Disorientation • Amnesia • Motor coordination • Balance deficits • Cognitive deficits • If ath has LOC • Must consider C-spine injury
Hx • Can you remember the score or who we played last week? (retrograde amnesia) • Can you remember walking off the field? (antegrade amnesia) • Does your head hurt? • Do you feel nauseous? • Do you have pain in your neck? • Can you move your arms and legs? • Do you remember what happened?
Observation • Does the athlete appear disoriented? • Does the athlete have a blank stare? • Does the athlete have incoherent speech? • Does the athlete respond to questions with delay? • Are they walking with imbalance? • Are they unable to focus? • How are they acting emotionally? • Is the athlete’s scalp swollen or bleeding? • Does the athlete have CSF coming out of their ear?
Palpation • ATC should palpate the following for obvious deformity… • Neck • Skull
Special Tests • Neurological Exam • Eye function • PERRLA • Nystagmus (demonstrate) • Balance Tests • Romberg • BESS (balance error scoring system) • Coordination Tests • Cognitive Tests • Remember these 5 words • Say the months backwards
Cranial Nerves • Review handout • Demonstrate
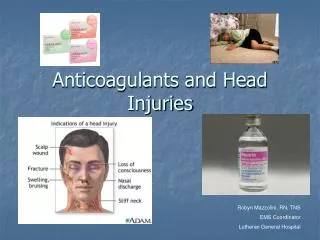
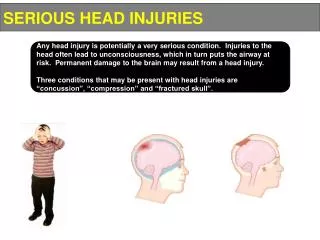
Skull FX • MOI: Direct blow to the head. • Examples… • Signs & Symptoms (S&S) • Severe headache • Nausea • Indentation in skull • Blood in ear or nose • “Battle’s sign” • “Racoon eyes” • CSF “Halo sign” • Management • Activate EMS • Refer to neurosurgeon ASAP • Why???
Cerebral Concussions • Definition: “Temporary impairment of brain function caused by impact to the head or by a rotational force.”
Concussions • MOI: • Direct blow • COUP injury vs Counter-coup • Acceleration/ deceleration forces causing the brain to shake.
Concussions S&S • Postraumatic Amnesia • Antegrade vs retrograde • Loss of balance • Behavior (not themselves) • Loss of CN function • Diminished neurological function • Confused • Vacant stare • Lack of focus • Delayed Responses • LOC • Emotions out of proportion • Slurred speech • Tinnitus • diplopia
Management • LOC, suspect C-Spine • Spine board and transport to ER via EMS • CT Scan • If no LOC • Evaluate on sideline • Track postconcussive signs and symptoms • Monitor vitals • NO ASPIRIN! • Not released until no s&s are present • Different scales • When to “grade” a concussion?
Grading Scale • Grade 1 • Grade 2 • Grade 3 • Different grading scales
Second-Impact Syndrome • Occurs when an ath sustains a 2ND blow to the head, while still recovering from a previous concussion. • Second blow can be minimal. • Causes swelling in the brain • ↑ intracranial pressure • Initially, ath appears normal • Moments later…. • Mortality rate of 50% • Management?
Cerebral Contusion • MOI: Impact with a stationary object • Causes bleeding in the brain. • S&S: • LOC • Headaches • Dizzyness • Nausea • Vomiting • Paralysis • Management: Refer to ER ASAP • CT Scan or MRI
Epidural Hematoma • Hematoma between the skull and dura mater. • S&S • Severe head pain • Dizziness • Nausea • Dilation of 1 pupil • Sleepiness • Management: Refer to ER • CT scan • Delayed medical attention can result in death or permanent disability • May be confused for mild concussion.
Subdural Hematoma • More common than epidural hematomas • Most common cause of death in athletes • Hematoma between the brain and dura mater. • MOI: deceleration/acceleration forces • S&S: same as epidural • No lucid interval • Management: • Activate EMS • Emergency!
Scalp Injuries • MOI: Blunt trauma causes laceration • Could cause brain injury • S&S: • Profuse bleeding due to high number of blood vessels in scalp • Makes it difficult to? • Pain • Management: Refer to ER • Requires stitches • CT scan to r/o brain injury
References • Prentice William: Arnheim’s Principles of Athletic Training, 12thed, New York,NY,2006, McGraw-Hill,246-269. • Cartwright AL: Fundamentals of Athletic Training, 3rded, Champaign, IL, 55-63