Adding Error Bars to Column and Bar Graphs in Excel
330 likes | 454 Vues
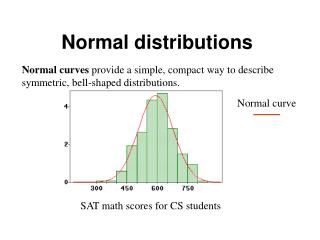
This guide explores the fundamental concepts of error bars in normal distributions, specifically how to add them to column and bar graphs in Excel. We cover the standard deviation as a measure of variability and demonstrate how to compute it alongside variance. Learn step-by-step methods to insert error bars, including selecting data points, formatting, and understanding systematic errors in your graphs. Enhance your data visualization skills while ensuring your representations accurately reflect variability in your datasets.

Adding Error Bars to Column and Bar Graphs in Excel
E N D
Presentation Transcript
Error Bars in Column / Bar Graphs http://chandoo.org/wp/2010/07/12/gantt-box-chart-tutorial-template/ http://support2.dundas.com/OnlineDocumentation/winchart2005/ErrorBarsChart.html
Standard Deviation, s Standard Deviation: A statistical measure of spread or variability. Computed as the root mean square (RMS) deviation of the values from their arithmetic mean. Variance: The square of the standard deviation. STDEV, sample of a larger population STDEVP, entire population
How to Add Error Bars 3 2 1 5 4
How to Add Error Bars Select the cell that contains the sigma value Type sigma here
(X,Y) Scatter Graphs & Regression Bad example Better example
How to Present (X,Y) Scatter Graphs, Compute Trendlines, and Extract Chemical Information using Excel Example: Chemical Kinetics & Equilibria SP10 Assign. #4 on Aspirin: Handout & online. SP11 Assign. #4 on pH-Indicator: Handout & online.
AP11 Assignment #4 Your simulated spectrum will be the sum of the Gaussian functions that describe the absorbances of the three species: -- protonated dye -- neutral dye, and -- deprotonated dye.
(X,Y) Data QF: Y-Axis Error Bars 1. Left click the graph line to which you want to add error bars. 2-Mac: Control-click the selected line. 2-PC: Left-click the selected line. 3. Select “Format Data Series”.
(X,Y) Data QF: Y-Axis Error Bars 3 1 2 4 5
(X,Y) Data QF: Types of Errors Systematic error: All numbers in the sample will be too high! The precise function was y = x2 The sample data were computed with: y = [x+0.3*RAND()]2 The x-values were assumed to be error-free The fitted function was: y = 0.9937x2+ 0.3459x The STDEV of the y-values is 0.62 Systematic error: There should not be a linear term. This is were you notice the systematic error made (on purpose) in the sample data generation!