The Circulatory System
210 likes | 375 Vues
The circulatory system is crucial for the transport of nutrients, gases, and waste within organisms. It can be classified into open and closed systems. In open circulatory systems, like those of insects and mollusks, hemolymph bathes organs directly. Conversely, closed circulatory systems, found in vertebrates, utilize blood confined within vessels. This intricate network includes the heart, arteries, capillaries, and veins, each playing vital roles in gas exchange and nutrient distribution. Understanding these systems is essential for comprehending cardiovascular health and diseases.

The Circulatory System
E N D
Presentation Transcript
The Circulatory System Natalie Janowiak, Anthony Storck, Emma Schwartz, Matt Gutt, Matt Gerber
Open Circulatory System • Blood directly bathes internal organs • Hemolymph- body fluid, same as blood and interstitial fluid • Heart pumps hemolymph through vessels into sinuses, where materials are exchanged with cells, and then returned to the heart
Ex) insects, arthropods, molluskssuch as crayfish and grasshoppers
Closed Circulatory System • Contains blood within vessels • Heart(s),blood vessels, blood • Heart pumps blood • Blood travels through vessels and into organs • Blood and interstitial fluids exchange materials
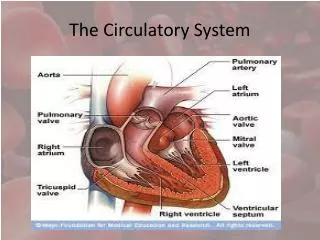
Parts of the System • Heart: a muscular pump to move the blood • Blood vessels: arteries, capillaries and veins that deliver blood to all tissues • Blood: a connective tissue.
Blood • Blood supplies oxygen, glucose, amino acids, and fatty acids to the tissues • It removes urea, carbon dioxide and lactic acid, • The blood coagulates which helps to stop bleedings • The blood transports hormones and signals tissue damage • It regulates body temperature and body ph • lood is made of red and white blood cells, platelets, and plasma • lood is made by bone marrow
Blood continued • Vertebrates all have closed circulatory systems • Mollusks and arthropods have an open circulatory system with hemolymph • Hemolymph is a combination of blood and interstitial fluid, composed of water, inorganic salts, and organic compounds. • In closed circulatory systems, hemolymph is separate from blood • Some animals such as flat worms have no circulatory system, but they have an extensive digestive system
Blood Vessels (Arteries) • Arteries are blood vessels that carry blood away from heart. • Arterial walls are able to expand and contract. • Arteries have three layers of thick walls. • Arteries branch off into arterioles.
Blood Vessels (Capillaries/ Veins) • Capillaries- branch off from arterioles • Microscopic vessels with thin, porous walls • Chemicals exchange between blood and interstitial fluid here • Capillaries converge into venules which lead into veins • Veins return blood to the heart
completely separates oxygen-rich and oxygen-depleted blood. 2 Atria/2 Ventricles Different blood not mixed Ex) Humans, birds, mammals Four Chambered Heart
Ex) Frog 2 Atria / 1 Ventricle Amphibian heart rate depends upon the outside temperature Three Chambered Hearts
Ex) Perch 1 Atrium/1 Ventricle Rudimentary valve located between the chambers Two Chambered Heart
Ex) Earthworm Simple structure, not a true heart Five arches Aortic Arches
Cardiovascular Diseases • Leading cause of death in the U.S. • Ex) heart attack, stroke, atherosclerosis, arteriosclerosis, hypertension (high blood pressure),
References • http://www.peteducation.com/article.cfm?cls=17&cat=1848&articleid=2951 • http://www2.gsu.edu/~bioasx/closeopen.html • http://www2.gsu.edu/~bioasx/closeopen.html