Short and Long Term Memory
170 likes | 513 Vues
Short and Long Term Memory. Chapter 3. Short Term Memory. Anything in your conscious mind at any one moment Does not necessarily involved paying close attention Repeating what someone said word for word Will not comprehend until you repeat it back Memory lasts as long as you hold it there

Short and Long Term Memory
E N D
Presentation Transcript
Short and Long Term Memory Chapter 3
Short Term Memory • Anything in your conscious mind at any one moment • Does not necessarily involved paying close attention • Repeating what someone said word for word • Will not comprehend until you repeat it back • Memory lasts as long as you hold it there • Numerous strategies to improve short-term memory
Rehearsal • Repetition of information • Mentally or out loud • Maintenance rehearsal • Keeps info in short term • Does not connect info to meaning • Elaborative Rehearsal • Transfer info to long term • Think about meaning • Connect to info already in storage
Practicing Rehearsal • 440-835-9471 • B H A N W O L K D • Sheep, phone, book, shoe, card, chip, drum
Chunking • Chunking puts items into groups • 1 group = 1 piece • 7 pieces of grouped items = greater memory • Phone numbers • 4408675309 vs 440-867-5309 • STM limited in duration and capacity • Can hold 5-9 pieces of information • Average is 7 • *Applies to unrelated items
Mnemonic Devices • Named after Greek goddess of memory Mnymosyne • Unusual associations made to material in order to aid memory • Not always logical • Replace rote memorization • If you can already make sense of the task at hand, don’t use a mnemonic device • Must be used from the beginning when learning info
Mnemonic Examples • King Henry Died Drinking Chocolate Milk • All Cows Eat Grass / FACE • Roy G. Biv • 30 Days Hath September, April, June, and November • In 1492 Columbus sailed the ocean blue • Never Eat Soggy Waffles • Please Excused My Dear Aunt Sally
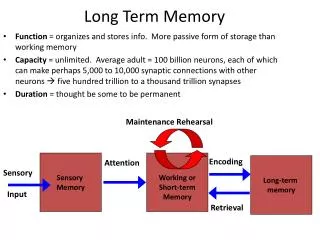
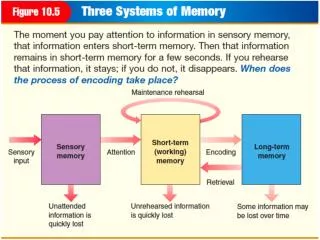
Long Term Memory • Sensory storage filters out the unnecessary • Short-term memory holds onto the knowledge needed right away • Information stored for future use • Representations of countless facts, experiences, and sensations • Holds onto ideas and themes
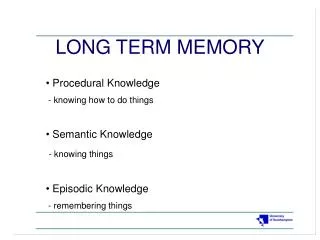
Types of memory Semantic Memory • Ideas and concepts not drawn from personal experience • Ex: Concept of a cat Explicit Memory* • Consciously recall and use as needed • Ex: Knowledge • Explicit memory used when taking a test • Episodic Memory • Memory of our own life • Ex: What you did this morning • Time of occurrence is important • Implicit Memory* • No conscious recall • Ex: Skills • Lose ability to describe tasks
Priming • Form of implicit memory • Information is learned • Cues given later to aid in recall • Ex: Fill in the blank question • First letter of the answer included
Schemas - Revisited • Long term memory organized into schemas • Brain is a filing cabinet with many drawers and each drawer has many folders • Way we mentally represent the world
Examples of Schemas • Same little girl sees a miniature horse and calls it a dog • Dogs are small, have four legs, and a tail • Parents explain that it is actually a very small horse • Modifies existing schema for horses to remember that they can be tall or short • Little girl sees a horse • Horse is tall, has four legs, and a tail • Sees a cow for the first time and calls it a horse • Cow is tall, has four legs, and tail • Modify existing schema for a horse and add new one for a cow
Prejudice • Existing schemas can inhibit learning • Prevents people from seeing the world as it really is • No new info taken in • Interpret situations incorrectly • Come up with alternate explanations of events that challenge pre-existing beliefs