VCU NMT Program Adrenal Scintigraphy
180 likes | 273 Vues
Learn about how adrenal cortical and medulla pathologies are evaluated with NP-59 and I131, including details on Aldosteronism, Addison’s, Cushing’s, and more. Discover insights on neuroblastomas and pheochromocytomas imaging techniques.

VCU NMT Program Adrenal Scintigraphy
E N D
Presentation Transcript
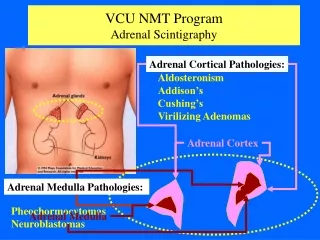
Adrenal Cortical Pathologies: Adrenal Cortex Adrenal Medulla Pathologies: Adrenal Medulla VCU NMT ProgramAdrenal Scintigraphy Aldosteronism Addison’s Cushing’s Virilizing Adenomas Pheochormocytomas Neuroblastomas
VCU NMT ProgramAdrenal Scintigraphy Adrenal cortical pathologies may be evaluated using NP-59, which is a form of cholesterol, labeled with I131. Since the adrenal cortex uses cholesterol to produce hormones, the adrenal cortex will concentrate the NP-59 labeled I131. NP-59 labeled I131 is rarely used in the clinical environment due to poor target to background ratios, poor imaging characteristics of I131, and difficulty in interpretation of results.
VCU NMT ProgramAdrenal Scintigraphy Specific points which you should remember: NP-59 should only be used for Adrenal Cortical pathologies. Before administering NP-59 the patient should be treated with Lugol’s solution which blocks thyroid uptake of free I131. Lugol’s administration should continue for 7 days. Administration of NP-59 I131 should be slow to prevent allergic reactions.
VCU NMT ProgramAdrenal Scintigraphy Adrenal Medulla imaging for determination of Medullar metastatic lesions is performed with I131 labeled mIBG, or I123 labeled mIBG which is not commercially available at this time. Detection of adrenal medulla activity is primarily used in the evaluation of neuroblastoma and pheochromocytoma.
VCU NMT ProgramAdrenal Scintigraphy Neuroblastoma is a form of cancer that usually occurs in infancy and childhood. The term neuro indicates "nerves," while blastoma refers to a cancer that affects immature or developing cells. Nearly 90% of cases are diagnosed by age 6. When detected early, neuroblastomas can usually be treated effectively. However, in as many as seven out of 10 cases, the disease is not diagnosed until it has already metastasized (spread). Overall, about 40% of children with neuroblastomas can be cured with a combination of surgery, followed by chemotherapy and/or radiation therapy.
VCU NMT ProgramAdrenal Scintigraphy Pheochromocytomas are vascular tumors of adrenal medulla tissue characterized by hypersecretion of epinephrine and norepinephrine. This condition puts the patient in a prolonged version of flight or flight and ultimately wears the body down. Pheochromocytomas may be found in the adrenal medulla or as metastatic tumors along the sympathetic ganglia (throughout the thorax and abdomen, but commonly along the vertebra and aorta).
1. antidepressants 2. antihypertensives 3. sympathomimetic: decongestants cocaine speed VCU NMT ProgramAdrenal Scintigraphy Specific points which you should remember: • mIBG should only be used for Adrenal Medulla pathologies. • Before administering mIBG the patient should be treated with Lugol’s solution which blocks thyroid uptake of free I131. • Lugol’s administration should continue for 6 -7 days. • Administration of NP-59 I131 should be slow to prevent reactions. • Many drugs interfere with uptake of mIBG in medulla tissue. • Normal areas of uptake include salivary glands, liver, spleen, heart, GI tract, and bladder. Obtain a complete list of medications and check with radiologist. • Sequential imaging should be performed to help identify normal vs. abnormal uptake. • Empty bladder before imaging.
Adrenal Medulla Pathologies: Pheochormocytomas Neuroblastomas VCU NMT ProgramAdrenal Scintigraphy Adrenal Cortical Pathologies: Aldosteronism Addison’s Cushing’s Virilizing Adenomas Review NP-59 mIBG
VCU NMT ProgramAdrenal Scintigraphy 24 hour mIBG I131 for Pheochromocytoma
VCU NMT ProgramAdrenal Scintigraphy 48 hour mIBG for Pheochromocytoma
VCU NMT ProgramAdrenal Scintigraphy 48 hour I131 mIBG for Neuroblastoma
E. VCU NMT Program 72 hour I131 mIBG 4 year old.
VCU NMT ProgramAdrenal Scintigraphy 48 hour I131 mIBG for Neuroblastoma
VCU NMT ProgramAdrenal Scintigraphy Neuroblastoma in 4 yo. Wide spread metastatic evolvement of bone marrow.
VCU NMT ProgramAdrenal Scintigraphy Metastatic Pheochromocytoma in liver
VCU NMT ProgramAdrenal Scintigraphy 48 hour I131 mIBG for Pheochromocytoma
VCU NMT ProgramAdrenal Scintigraphy Generally, Neuroblastomas are imaged at 48 and 72 hours with I131 mIBG. Pheochormocytomas are generally imaged at 24 and 48 hours. The timing difference is largely due to Pheochromocytomas being much more vascular; therefore, they demonstrate more rapid accumulation of the radiopharmaceutical. Sequential imaging (subsequent days days) helps to distinguish normal vs abnormal uptake. How?
End of Lecture Return to the Table of Content