Geometric Random Variables
130 likes | 356 Vues
This document explores fundamental concepts of geometric and Poisson random variables, focusing on their definitions, probability mass functions (pmf), and properties. The geometric random variable represents the number of Bernoulli trials until the first success, with its pmf defined as f(k) = (1-p)^(k-1)p. It highlights the memoryless property, demonstrating how future probabilities are independent of past trials. For Poisson random variables, representing events over a fixed time period, it reviews the pmf and characteristics of rate parameters. Key applications include understanding these distributions in practical scenarios like queuing and inventory management.

Geometric Random Variables
E N D
Presentation Transcript
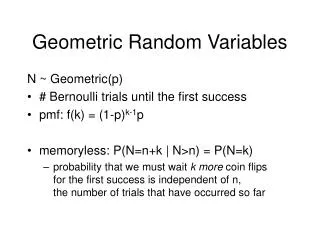
Geometric Random Variables N ~ Geometric(p) • # Bernoulli trials until the first success • pmf: f(k) = (1-p)k-1p • memoryless: P(N=n+k | N>n) = P(N=k) • probability that we must wait k more coin flips for the first success is independent of n,the number of trials that have occurred so far
Previously… • Conditional Probability • Independence • Probability Trees • Discrete Random Variables • Bernoulli • Binomial • Geometric
Agenda • Poisson • Continuous random variables: • Uniform, Exponential • E, Var • Central Limit Theorem, Normal
Poisson N ~ Poisson() • N = # events in a certain time period • average rate is • Ex. cars arrivals at a stop sign • average rate is 20/hr • Poisson(5) = #arrivals in a 15 min period
Poisson • pmf: P(N=k) = e- k/k! • Excel: POISSON(k,,TRUE/FALSE) =3 =12.5
Poisson N1~Poisson(1), N2~Poisson(2) • N1+N2 ~ Poisson(1+ 2) • Splitting: • Poisson() people arrive at L-stop • probability p person is south bound • Poisson(p) people arrive at L-stop south bound
other slides… from Prof. Daskin’s slides
Xrandom variable E[g(X)]=∑k g(k) P(X=k) E[a X+b] = aE[X] +b Var[a X + b] = a2 Var[X] always X1,…,Xn random variables E[X1+…+ Xn] = E[X1]+…+E[Xn] always Var[X1+…+ Xn] = Var[X1]+…+Var[Xn] when independent E[X1·X2·…· Xn] = E[X1]·E[X2] ·…·E[Xn] when independent E and Var
X~Bernoulli(p) E[X]=p, Var[X]=p(1-p) X~Binomial(N,p) E[X]=Np, Var[X]=Np(1-p) N~Geometric(p) E[N]=1/p, Var[N]=(1-p)/p2 N~Poisson() E[N]= , Var[N]= X~U[a,b] E[X]=(a+b)/2, Var[X]=(b-a)2/12 X~Exponential() E[X]=1/, Var[X]=1/2 E, Var
Central Limit Theorem X1,…,Xn i.i.d, µ=E[X1], 2=Var[X1] • independent, identically distributed Sn = X1,…,Xn • E[Sn]=nµ, Var[Sn] = n2 • distribution approaches shape of Normal • Normal(nµ,n2)
=1 =2 =4 Normal Distribution mean=0
Normal Distribution X1 ~ N(µ1,12), X2 ~ N(µ2,22) • X1+X2 ~ N(µ1+µ2,12+22) • pdf, cdf NORMALDIST(x,µ,,TRUE/FALSE) • fractile / inverse cdf • p=P(X≤z) • NORMINV(p,µ,)
Newsvendor Problem • must decide how many newspapers to buy before you know the day’s demand • q = #of newspapers to buy • b = contribution per newspaper sold • c = loss per unsold newspaper • random variable D demand