Plant Structures
160 likes | 396 Vues
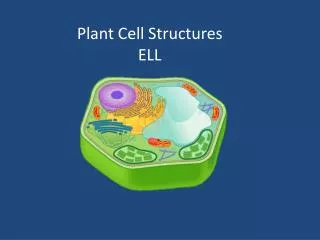
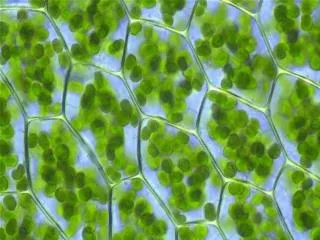
Plant Structures. A study of plant anatomy. Review. Eukaryotic Multi-cellular Autotrophic Evolved from green algae Make their own food through photosynthesis Light + H 2 O + CO 2 C 6 H 12 O 6 + O 2 Occurs in organelles called chloroplasts. Plant Structure: Organs. Plant organs.

Plant Structures
E N D
Presentation Transcript
Plant Structures A study of plant anatomy
Review • Eukaryotic • Multi-cellular • Autotrophic • Evolved from green algae • Make their own food through photosynthesis • Light + H2O + CO2 C6H12O6 + O2 • Occurs in organelles called chloroplasts
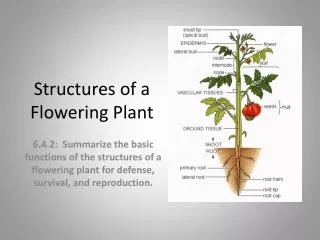
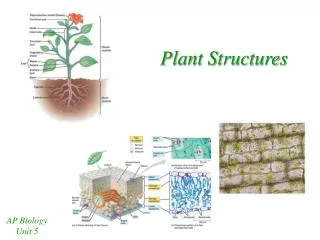
Plant Structure: Organs • Plant organs • Organs composed of 1 or more tissues • 3 major types: • roots • stems • leaves • Flowers and fruits evolved from stems and leaves
Most water absorbed by root hairs Plant Structure: Roots • Uptake of water and nutrients • Main functions of roots • Anchor and support • Water and nutrient uptake • Root hairs are projections of epidermal cells • Substantially increase surface area of roots
Plant Structure: Stems • Functions • Support leaves, flowers, fruits • Stems • Transport of water (xylem)and products of photosynthesis (phloem) • Storage of carbohydrates
Plant Structure: Stems • Stems used only for asexual reproduction • Stolon (or runner) = horizontal stem that arises from leaf axil and runs above ground (e.g. strawberry, spider plant) • Stems • When tip of stolon hits ground a new plant forms
Plant Structure: XYLEM & PHLOEM • Xylem: specialized tissues that transport water & minerals from the roots to the stem • Phloem: specialized tissue that transport glucose (food) from the leaf to other areas of the plant’s body • Collectively called “vascular bundle”
Plant Structure: XYLEM & PHLOEM Phloem - DOWN Xylem - UP
Plant Structure: Leaves Leaves come in variety of shapes and sizes Vary among plants and may be used for identification. Leaves are arranged in different ways Provides a large surface area to trap sunlight needed for photosynthesis The food factory of the plant
Plant Structure: Leaves • Main sight of photosynthesis • Covered by epidermis and cuticle • Create water proof barrier
Plant Structure: Leaves The cuticle is a non-cellular protective layer covering the outer cell layer (epidermis) of the green, aerial parts of land plants.
Plant Structure: Leaves Transpiration is a process where water (H2O) leaves a plant through stomata.
Plant Structure: Leaves Stomata Small opening, on the underside of a leaf, where CO2 enters the plant AND where O2 and H2O leave the plant in a process called transpiration.