Ionic Bonding: Metals and Non-Metals Interactions<br>
180 likes | 218 Vues
Learn how ions are formed through gain or loss of electrons in ionic bonding, the role of metals and non-metals, and properties of ionic compounds. Discover how atoms with varying valence electrons create stable compounds.<br>

Ionic Bonding: Metals and Non-Metals Interactions<br>
E N D
Presentation Transcript
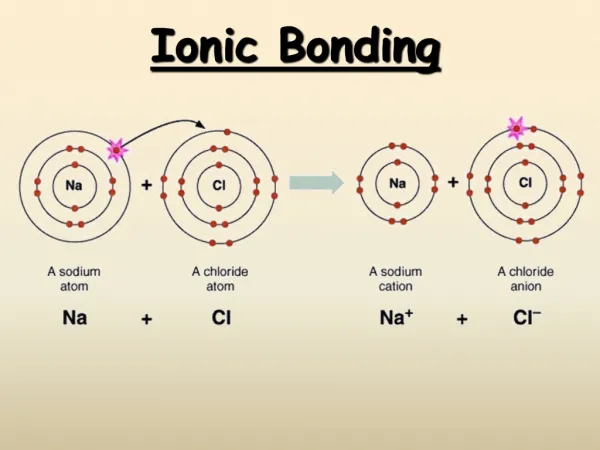
Ions Are atoms that have gained or lost e- An atom that gains e- becomes negatively charged and is called an anion An atom that loses e- becomes positively charged and is called a cation
How metals form ions Metals atoms typically have 1 valence e- (Group 1) or 2 valence e- (Group 2 and transition metals) or 3 valence e- (Group 13) According to the octet rule, they will lose these e- to form cations
How metals form ions Group 1 metals form +1 cations Li +1 Na +1 Group 2 and transition metals form +2 cations Mg +2 Ca+2 Fe+2
How non metals form ions Non metals typically have 4 or more valence e-. Group 14 elements (4 valence e-) do not tend to form ions, they tend to form covalent bonds
How non metals form ions Group 15 (5 valence e-) tend to gain 3 e- for a total of 8 valence e- N -3 Group 16 (6 valence e-) tend to gain 2 e- O-2 Group 17 (7 valence e-) tend to gain 1 e- F-1 What about Group 18?
What atoms from ionic bonds? 1) a metal and a non metal 2) Atoms with an electronegativity difference greater than 1.7 3) Polyatomic ions (see Table E, the place to be…)
Forming an ionic bond Its simple! The metal gives its e- (s) to the non metal. Both atoms end up with a noble gas e- configuration (full valence shell)
Na Cl
+ Na Cl -
Once the e- is transferred, the anion and cation are attracted to each other, and form a stable compound - + Cl Na
Compounds with polyatomic ions Polyatomic ions are charged groups of 2 or more covalently bonded atoms (SO4) -2 = sulfate ion These can form an ionic bond with other ions Ca+2 + (SO4) -2 Ca (SO4)
Making neutral ionic compounds The positive charge on the cation MUST EQUAL the total positive charge on the anion
Ionic compounds Do not have MOLECULES They have a crystal lattice of alternating + and - ions
Molecules Ionic compound crystal lattice
Properties of ionic compounds • Hard • High melting point • High boiling point • Poor conductors as solids • Ok conductors when melted (liquids) even though there are no mobile e- ions become mobile, but are heavier than e-, so they move slower