Menstrual Cycle
290 likes | 846 Vues
The menstrual cycle is a regular natural change that occurs in woman’s body approximately in monthly cycles throughout her reproductive life. It occurs in the reproductive system of a female, specifically in the uterus and ovaries which are responsible to make pregnancy possible.<br>https://www.novaivifertility.com/primary-offering/basic/ivf

Menstrual Cycle
E N D
Presentation Transcript
MENSTRUAL CYCLE MENSTRUAL CYCLE
2 The Menstrual Cycle The Menstrual Cycle § Rhythmical series of physiological changes that occur in fertile women § Includes a series events which occur about every 28 days throughout child bearing age of 35 years § Under the control of the endocrine system § Necessary for reproduction § & cervix The cycle consists of changes taking concurrently in the ovaries, uterus
© 2012 NOVA IVI FERTILITY | 3 Phases of the Menstrual Cycle • Menstrual cycle can be divided into 3 phases: – Menstrual Phase – Proliferative / Follicular (Estrogen) Phase – Secretory / Luteal Phase (Progesterone) Phase
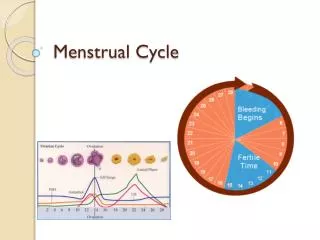
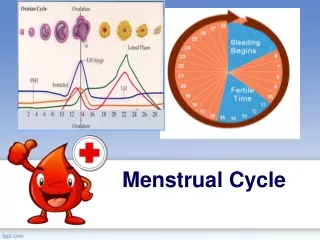
4 Average start and end day (assuming a 28-day cycle) Phase Menstrual phase 1-4 Proliferative phase 5-13 Ovulation 13-16 Secretory phase 16-28
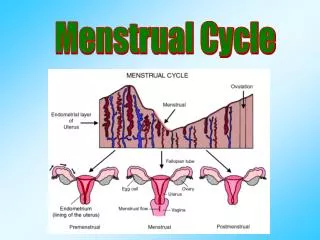
5 Menstrual Menstrual Cycle…Diagrammatic Cycle…Diagrammatic Representation Representation
6 The Menstrual Cycle The Menstrual Cycle Anterior lobe of the pituitary -- secretes FSH -initiates growth of the follicle in the ovary. 3 As the ovum matures the follicle secretes estrogen which is necessary for the growth of the Endometrium & to receive the fertilized ovum 3 At peak levels of estrogen --FSH secretion is prevented & LH is secreted by the anterior pituitary 3 Midcycle LH surge is responsible for ovulation 3 Following ovulation LH converts the ruptured follicle into corpus luteum which secretes progesterone 3
9 Pituitary Hormones
10 Changes in the Ovaries Stage 2 - Egg Continues To Ripen; Follicle Growth. Stage 3 - Ovulation Fully Mature Egg Bursts Out Of Follicle. Stage 1 – Ovum Begins To Develop. Stage 4 - Egg Enters Fallopian Tube Follicle Remains And Forms The Corpus Luteum.
11 Changes in the Ovaries: • Stage 1 - An egg is beginning to mature within a cluster of cells called a follicle • Stage 2 - Rapid follicle and egg growth • Stage 3 - Ovulation occurs; fully mature egg bursts out of the follicle (fertile) empty follicle transforms into the corpus luteum • Stage 4 - Egg travels through fallopian tube (7 days) if not fertilized upon arrival in uterus the corpus luteum shrinks triggering menstruation and ripening of new egg.
12 Changes in Ovarian Hormones: • Estrogen -gradually increases during days 1-14; signals body to thicken the lining of the uterus. Levels drop sharply after ovulation. • Progesterone -Levels remain low during the first half of the cycle and then increase sharply during the second half of the cycle. Maintaining the growth of the endometrium lining.
13 Changes in the Uterus: Stage 2 Day 5- 13 pre-ovulatory stage Stage 1- Day 1-5 menstruation Stage 3 Day 14 Ovulation Stage 4 Day 15-28 post-ovulatory stage
14 The uterine lining slowly thickens from day 5 through day 28
15 Changes in the Uterus: • Stage 1- Menstruation- Endometrium breaks down and blood, mucus, tissue, and the egg are shed through the vagina. • Stage 2- Menstrual flow stops & endometrium begins to thicken. • Stage 3- Endometrium continues to thicken. • Stage 4- The endometrium is at it’s thickest point.
24 No Of Ovarian Follicles No Of Ovarian Follicles 320 weeks gestation 7,000,000 3 At birth 1,000,000 3 At puberty 400,000 3 Fertile age approx... 475 will ovulate
25 Menopause • The time when processes, which occur at puberty, are reversed. • The ovaries gradually becomes less responsive to the FSH and LH. • Ovulation and menstrual cycle become irregular and eventually ceases. • Female secondary sex characters begin to regress.
© 2012 NOVA IVI FERTILITY | THANK YOU