Catalyst
180 likes | 362 Vues
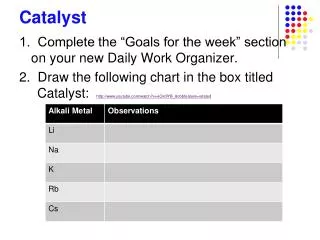
Catalyst. 1. 2. 3. Lecture 6.2 – Calculating ΔG and ΔG o. Today’s Learning Targets. LT 6.4 – I can calculate ΔG and ΔG o for a given set of ΔH and ΔS values. Furthermore, I can interpret this result to determine if a reaction is spontaneous or non-spontaneous .

Catalyst
E N D
Presentation Transcript
Catalyst 1. 2. 3.
Today’s Learning Targets • LT 6.4 – I can calculate ΔG and ΔGo for a given set of ΔH and ΔS values. Furthermore, I can interpret this result to determine if a reaction is spontaneous or non-spontaneous. • LT 6.5 – I can calculate ΔGo from standard free energies of formation (ΔGof) for a given chemical reaction.
Calculating ΔG • Recall, for any chemical reaction, the free energy can be calculated as long as ΔH and ΔS are known • ΔGo can be calculated under standard state conditions (using ΔHo and ΔSo) • Note ΔH is usually in kJ and ΔS is usually in J/K. • You need to convert before doing the calculation!
Class Example • Calculate ΔG for the following reaction: • N2 (g) + O2(g) 2 NO (g) • given that ΔH = 180.7 kJ and ΔS = 24.7 J/K. Is the reaction spontaneous or not spontaneous?
Table Talk • Calculate ΔGo for a reaction for which ΔHo = 24.6 kJ and ΔSo= 132 J/K at 298 K. Is the reaction spontaneous under these conditions?
Stop and Jot • For the following reaction: 2 POCl3 (g) 2 PCl3 (g) + O2 (g) • Given that ΔHo = 572 kJ and ΔSo = 179 J/K. At what temperature does this reaction become spontaneous?
Standard Free Energies of Formation (ΔGfo) • The standard free energy of formation (ΔGfo) is the change in free energy when we take elements in their standard state to make a compound. • Same idea as ΔHfo • WE can use these to calculate ΔGo even when ΔSo and ΔHo are unknown.
Class Example • Calculate ΔGo for the following reaction: P4 (g) + 6 Cl2 (g) 4 PCl3 (g) • Given that the reaction is at 298 K and the following ΔGfo: • P4 (g) = 24.4 kJ/mol • PCl3 (g) = -269.6 kJ/mol
Table Talk • Calculate ΔGo for the following reaction: CH4 (g) + 2 O2 (g) CO2 (g) + 2 H2O (g) • Given that the reaction is at 298 K and the following ΔGfo: • CH4 = -50.8 kJ/mol • H2O = -237.13 kJ/mol • CO2 = -394.4 kJ/mol
Stop and Jot • Calculate ΔGo for the following reaction: 2 PbS (s) + 3 O2 (g) 2 PbO (s) + 2 SO2 (g) • Given that the reaction is at 298 K and the following ΔGfo: • PbS = -152.4 kJ/mol • PbO = -187.9 kJ/mol • SO2 = -300.4 kJ/mol
Relay Race Questions 1. Predict the conditions (if any) under which the following reaction will be spontaneous: 2 SO2 + O2 2SO3 + 56 kJ 2. For a certain chemical reaction ΔHo = -35.4 kJ and ΔSo = -85.8 J/K. Determine if the reaction is spontaneous at 298 K. 3. For the following reaction: N2 (g) + 3F2 (g) 2NF3 (g) Given that ΔH = -249 kJ and ΔS = -278 J/K, at what temperature does the reaction become spontaneous? 4. Determine ΔGo for the following reaction: 2 H2O2 (l) 2 H2O (l) + O2(g) 5. Determine ΔGo for the following reaction: CH4 (g) + 4 F2 (g) CF4 (g) + 4 HF (g)
Drill Baby Drill • For the next 45 minutes you may work on the following: • ΔG calculation drills • ΔGf calculation drills • ΔG, ΔS, and ΔH integrated practice • Free Response ΔG Problems (only do if you have completed the integrated practice) • Short quiz during the last 15 minutes of class!
Quiz • Take 15 minutes to complete the quiz on Thermodynamics
Rate Yourself • Using your learning target log, rate yourself 1 – 4 on 6.1 and 6.5
Read 19.5 and 19.6 • Complete the free response practice for Monday/Tuesday Closing Time