Understanding Lipids: Types, Functions, and Structures
120 likes | 221 Vues
Learn about the diverse families of lipids including fats, phospholipids, and steroids, their vital functions in energy storage, cell structure, and more. Understand the structures of triglycerides, fatty acids, phospholipids, and steroids, and the differences between saturated and unsaturated fats. Discover how these molecules impact health and the risk of cardiovascular disease. Dive into the fascinating world of lipids with this comprehensive guide.

Understanding Lipids: Types, Functions, and Structures
E N D
Presentation Transcript
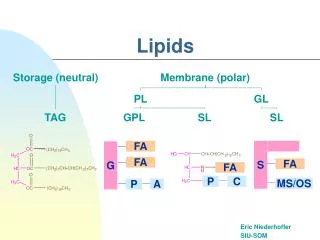
LIPIDS • Families of lipids include fats, phospholipids, and steroids; made up mostly of hydrocarbons. • These families above DO NOT mix with water
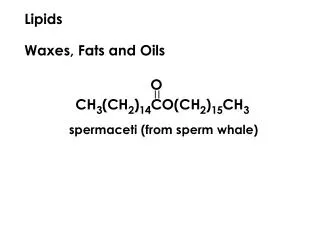
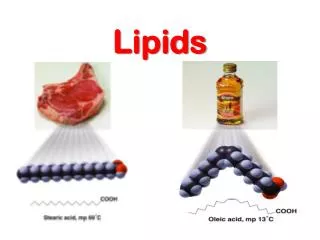
LIPIDS • Major function is for energy and nutrient storage (A gram of fat stores more than twice as much energy as a gram of a polysaccharide.) • Insulation, protect internal organs, hormones, used to make up cell membrane • Fat molecules are made up of four parts: • a molecule of glycerol (on the right) and • three molecules of fatty acids. • This structure forms a triglyceride. • Glycerol is a 3 carbon alcohol • Fatty Acids have LONG carbon skeletons that range in length
Fatty acids • A hydrocarbon chain with an acidic –COOH group at one end that attaches to the glycerol molecule. • Since the other unattached end of the fatty acid is –CH, it is a non-polar molecule and will not attract polar molecules such as water hydrophobic
Saturated FATS • Have the maximum number of the hydrogen atoms at each carbon (no double bonds); as many hydrogens as possible bonded to the carbon skeleton • Most fats present in animals ie. Cows, sheep • Solid at room temp. • It contributes to cardiovascular disease since their structure is “saturated”
Unsaturated FATS • Have one or more DOUBLE BONDS; has one or more double bonds and will have a kink in its tail wherever there is a double bond. • Examples: Plant fats • Liquid at room temp. • Fat from plants and fishes are generally unsaturated and are liquid at room temperature – they are oils. Double Bond
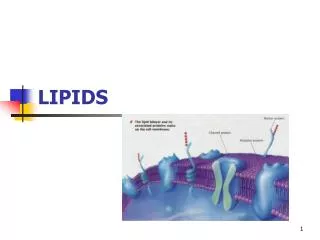
Phospholipids • Phospholipids are similar to fats, but they only have two fatty acids tails. • The 3rd carbon is attached to a phosphate group (water loving) • When phospholipids are added to water, they self assemble • into micelles: a phospholipid droplet with the hydrophobic • tails inside and the hydrophilic heads facing the water. • Heads are hydrophillic (water loving) • Tails are hydrophobic (water hating) • Cell membrane is made of 2 layers of phospholipids
Steroids • Made of a CARBON skeleton of 4 fused rings • Cholesterol is an important steroid for the body, in animal cell membranes • It is the precursor for the production of other steroids and hormones
Steroids • BUT a high concentration of cholesterols causes ARTHEROSCLEROSIS which can eventually lead to heart attacks!! Oh No!